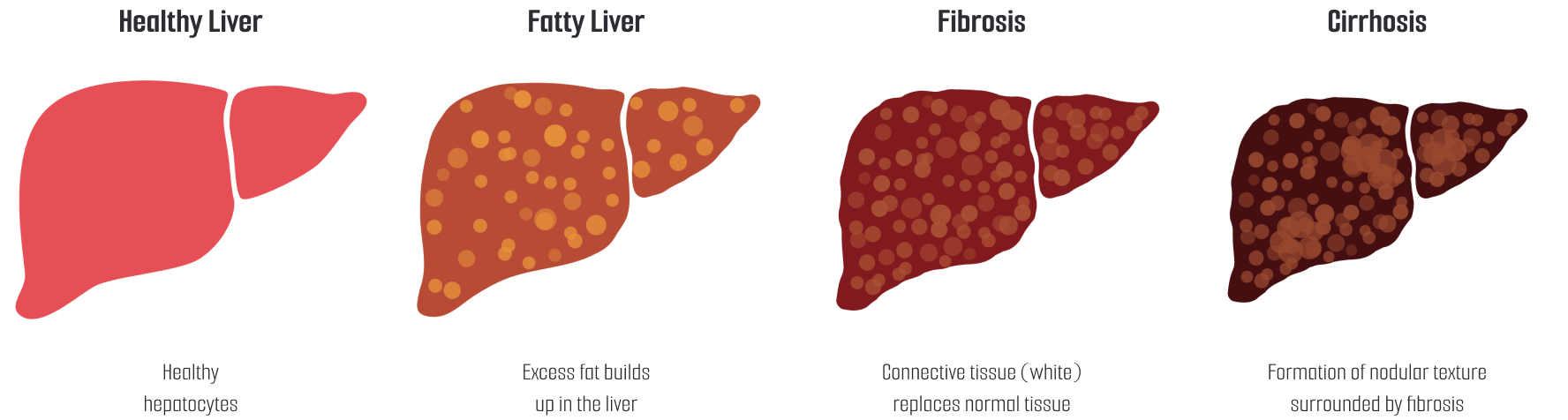
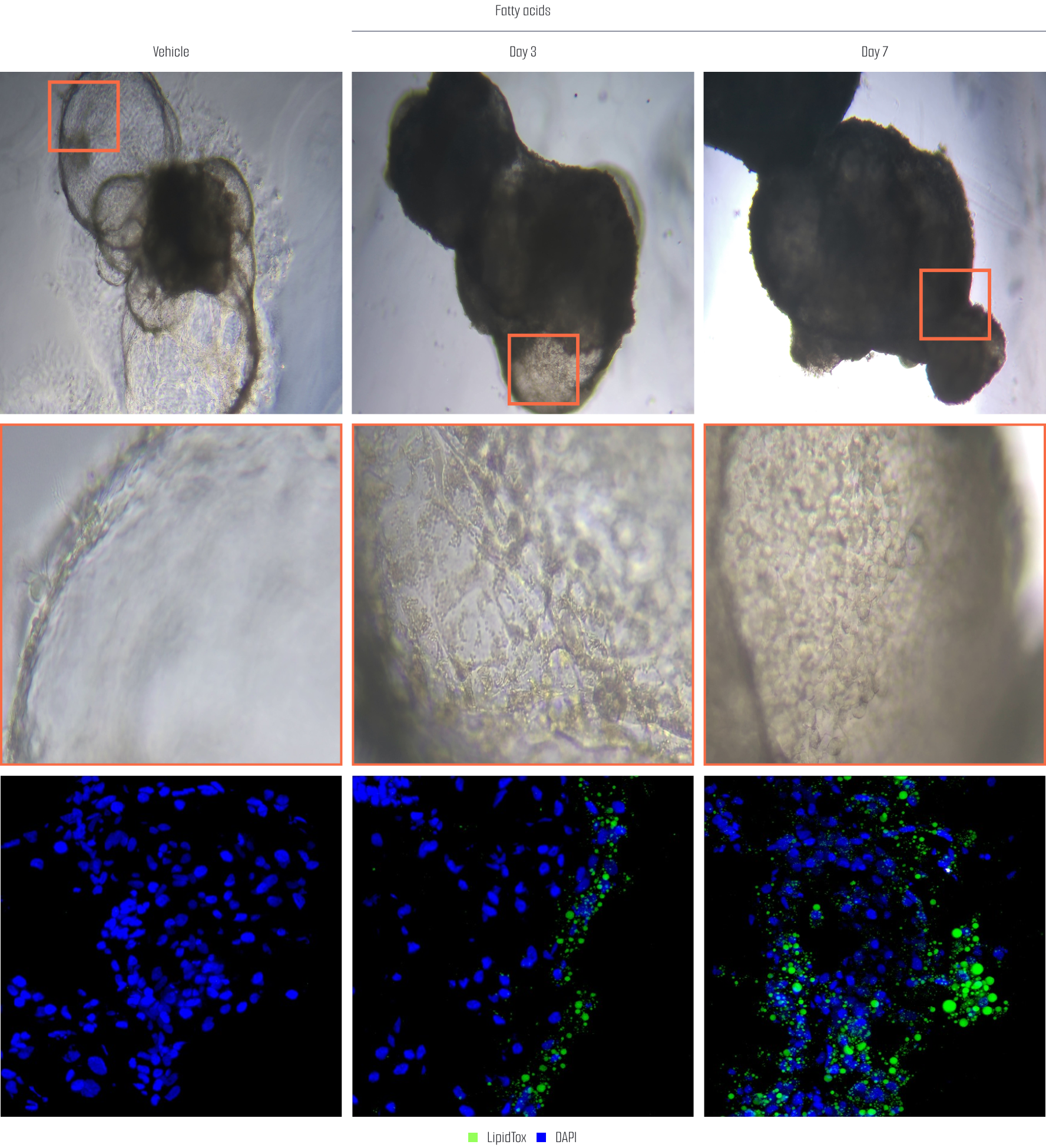
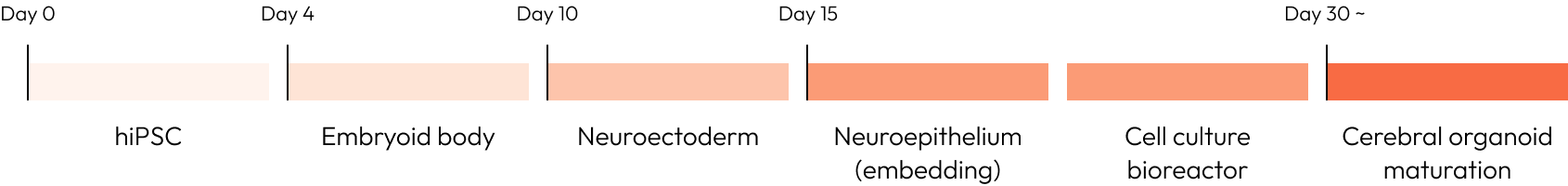Meet us at AACR 2026 - April 17-22 - TME Interplay with Organoids
Meet us at AACR 2026 - April 17-22 - TME Interplay with Organoids
Meet us at AACR 2026 - April 17-22 - TME Interplay with Organoids
Meet us at AACR 2026 - April 17-22 - TME Interplay with Organoids
Meet us at AACR 2026 - April 17-22 - TME Interplay with Organoids
Meet us at AACR 2026 - April 17-22 - TME Interplay with Organoids