Price | 2830€+ Login to see price |
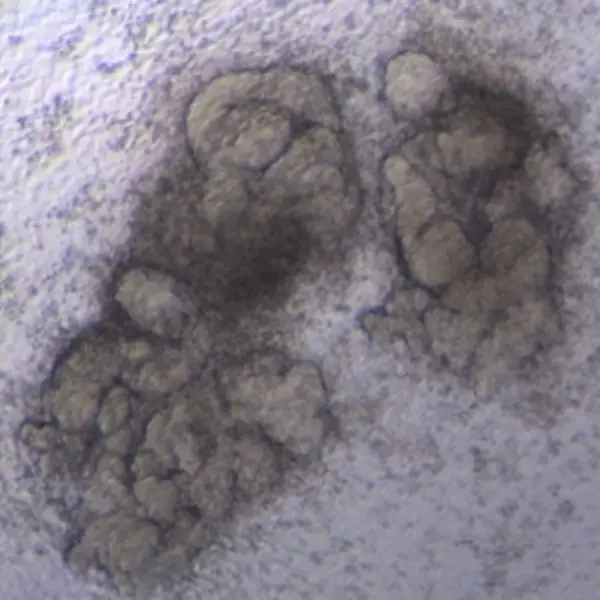
Organism | Human |
Product Type | iPS-derived organoid |
Tissue | Kidney |
Disease | – |
Applications
Toxicity
Organoid Based
Disease Modeling
Metabolic Disease Model

With the global rise of K-beauty, the cosmetics industry continues to grow steadily. Since the ban on animal testing for cosmetics in Korea in 2017, various alternative testing methods have...

Traditional microscopy methods often require fluorescent labeling to analyze cellular structures, which can be time-consuming and invasive. In contrast, our HT-X1 system allows for high-resolution visualization of cellular morphology without...

Traditional protein analysis has primarily focused on quantifying expression levels within tissue samples. However, recent advances in spatial analysis techniques have shifted attention toward evaluating not only expression levels, but...
Among the many fermented foods we consume, kimchi is particularly known for containing a diverse range of lactic acid bacteria, which are believed to influence the activation of immune cells...
We conducted a study focused on identifying disease-related markers using patient-derived tissue samples. However, traditional methods limited our ability to analyze multiple candidate markers simultaneously, and the limited availability of...
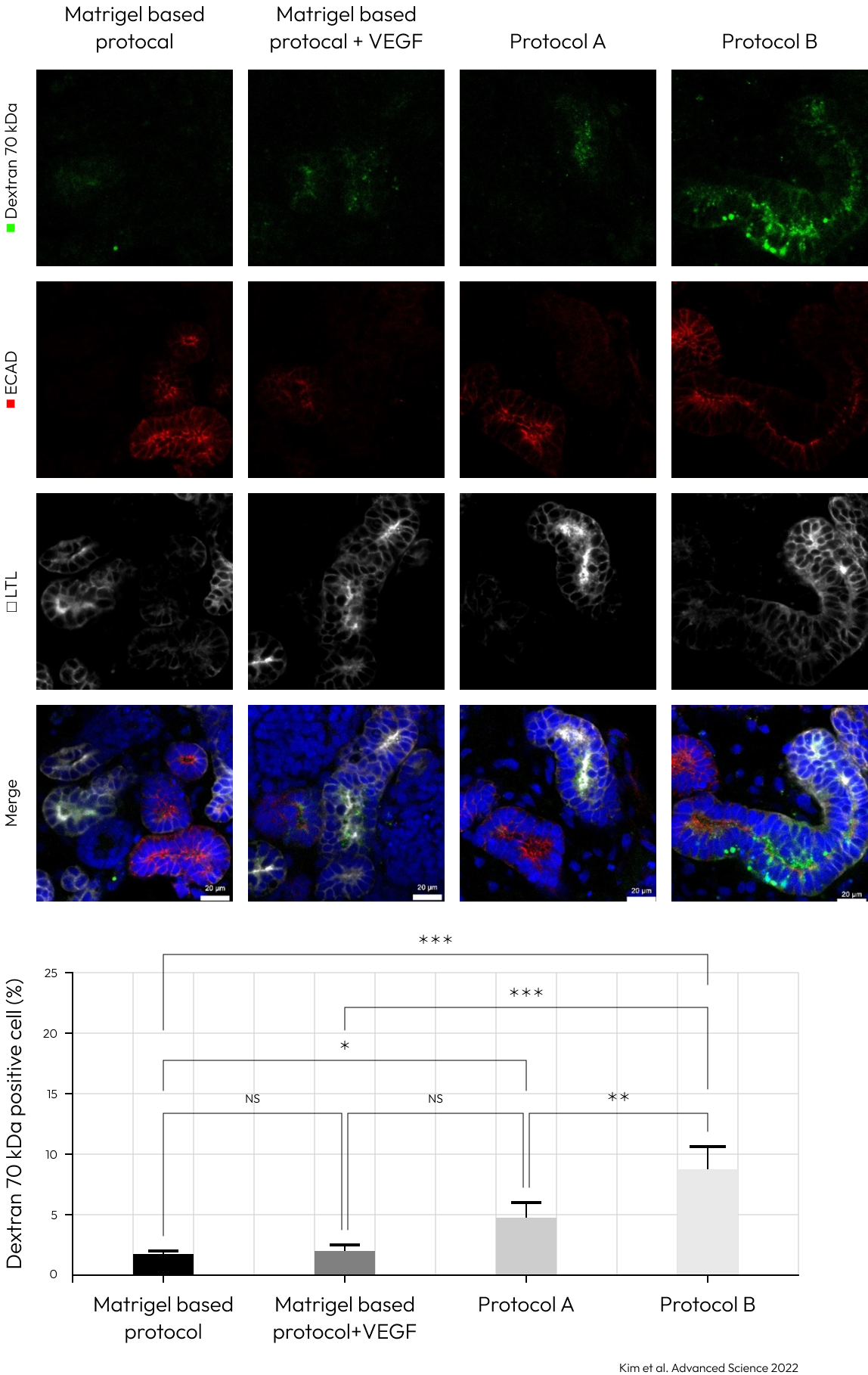
The kidney organoids generated by protocols A and B had tubular structures, and their size was greater than the kidney organoids without kidney dECM.
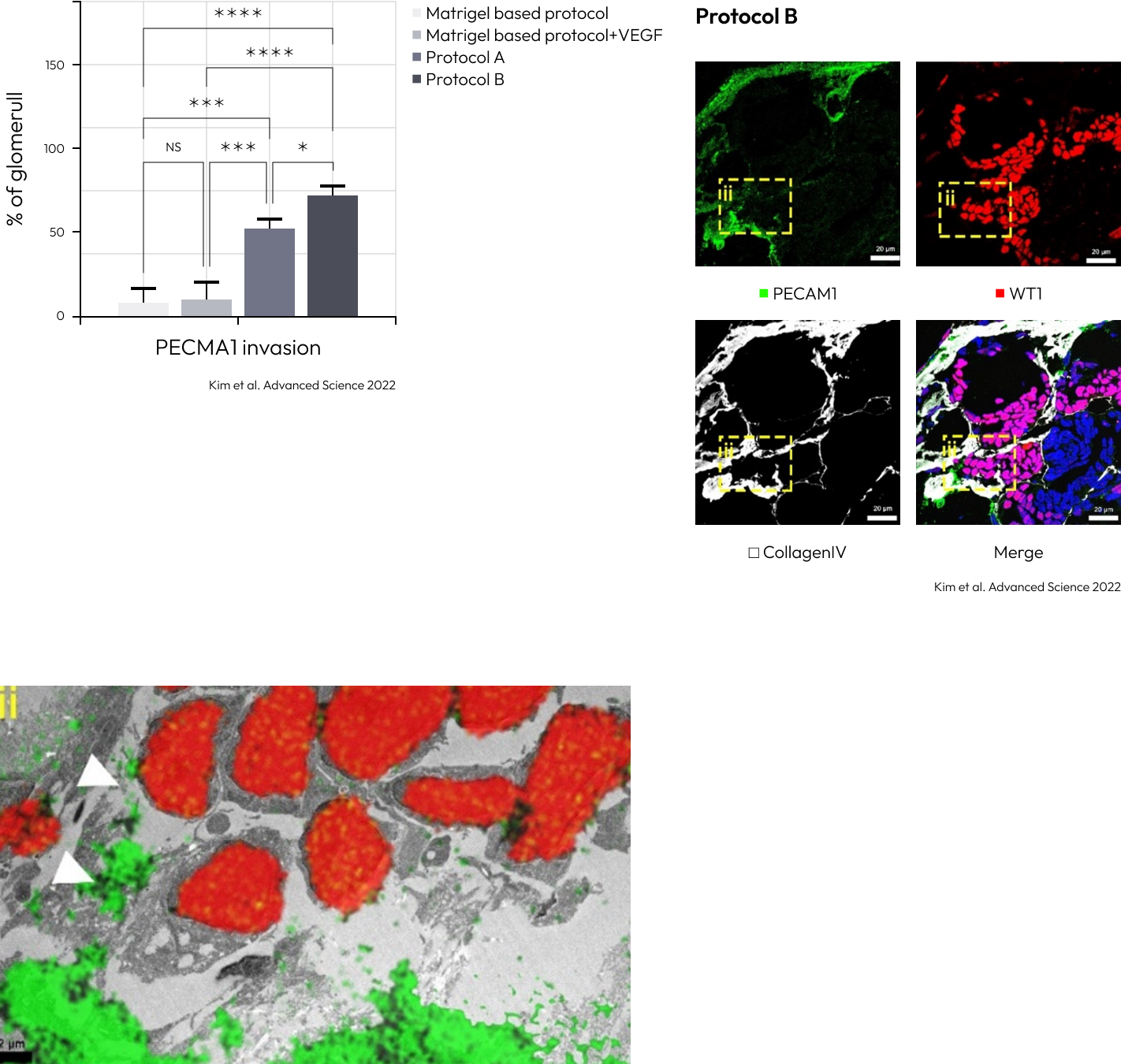
The vascularization was extensively increased in the kidney organoids gen-erated by protocol A, and accelerated in those generated by protocol B.
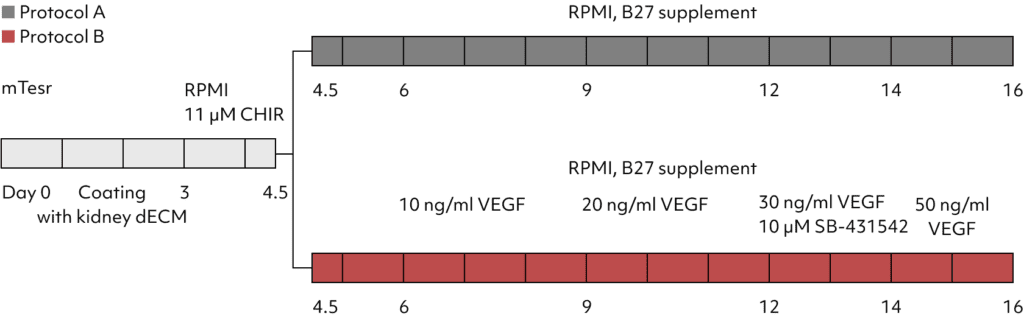
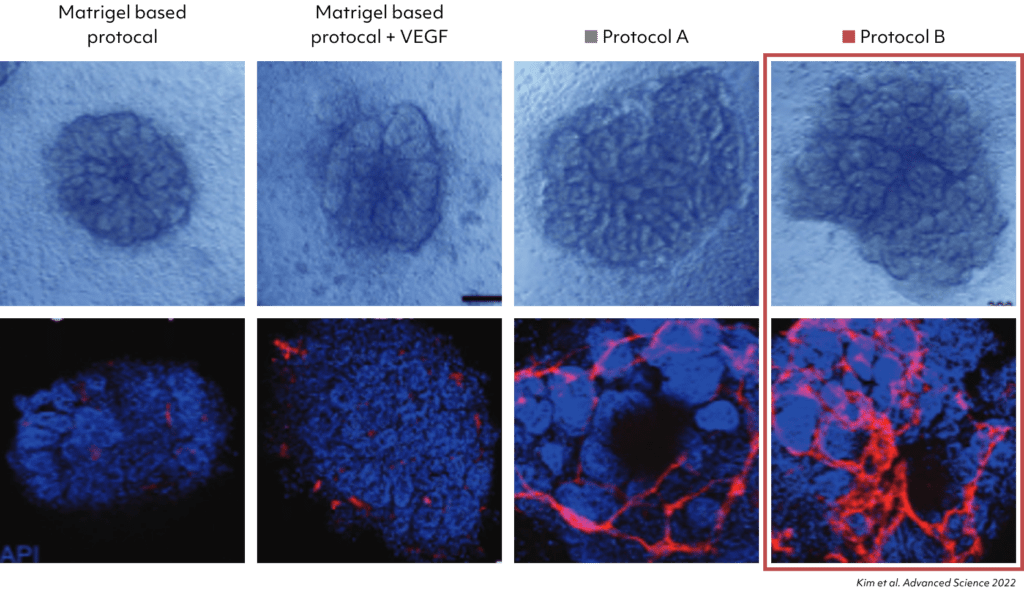
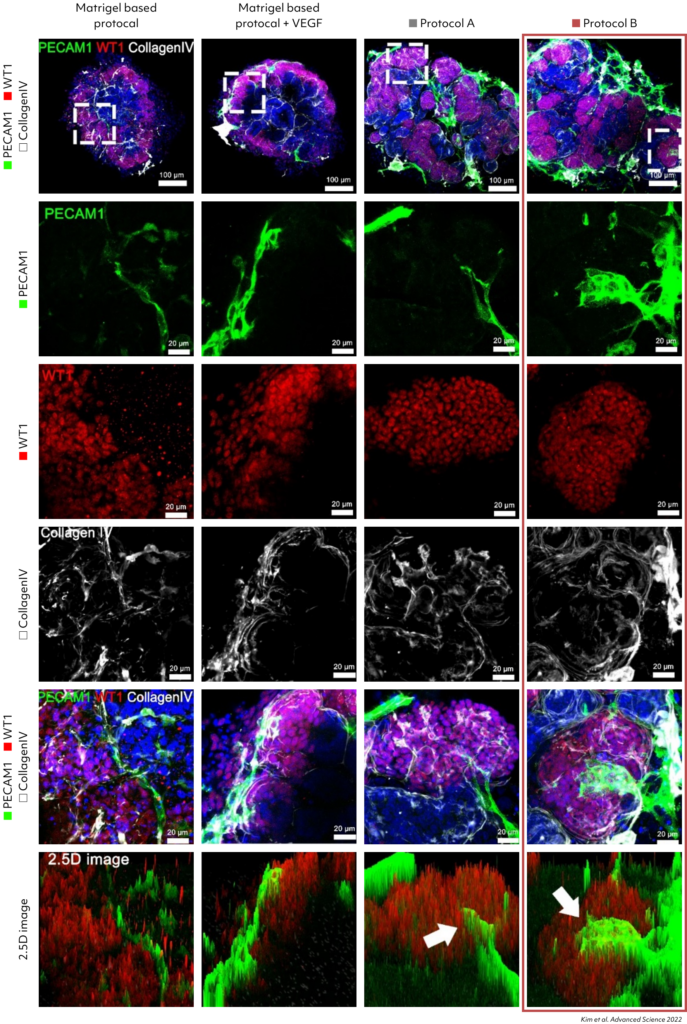
Confirmation of increased PECAM1expression in Kidney Organoids grown with Protocol B. Increased vascular network observed in the new differentiation protocol.
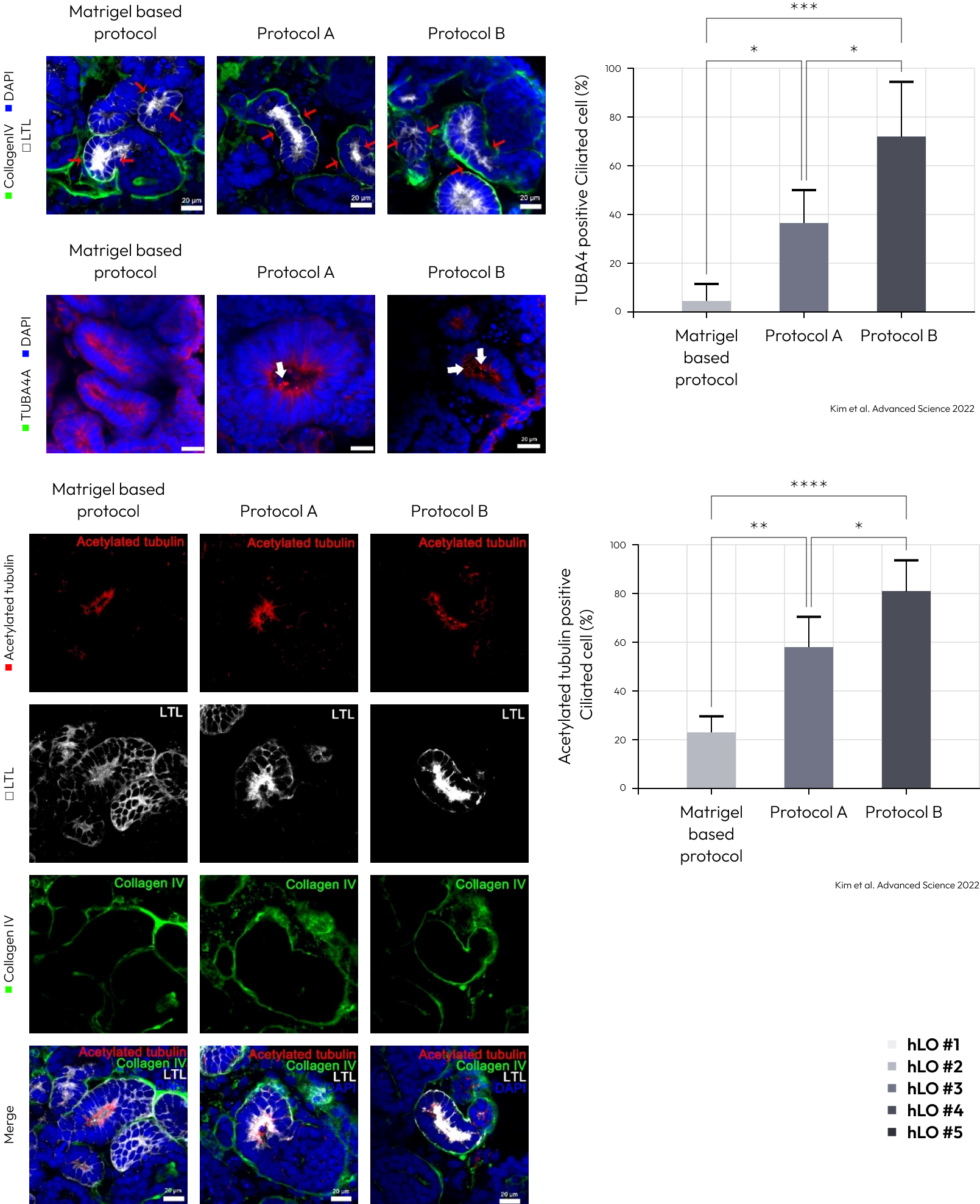
Enhanced polarization of the proximal tubules, with apical enrichment of the brush border marker lotus tetragonolobus lectin (LTL) and primary cilia, was observed in kidney organoids cultured by protocol A and B.
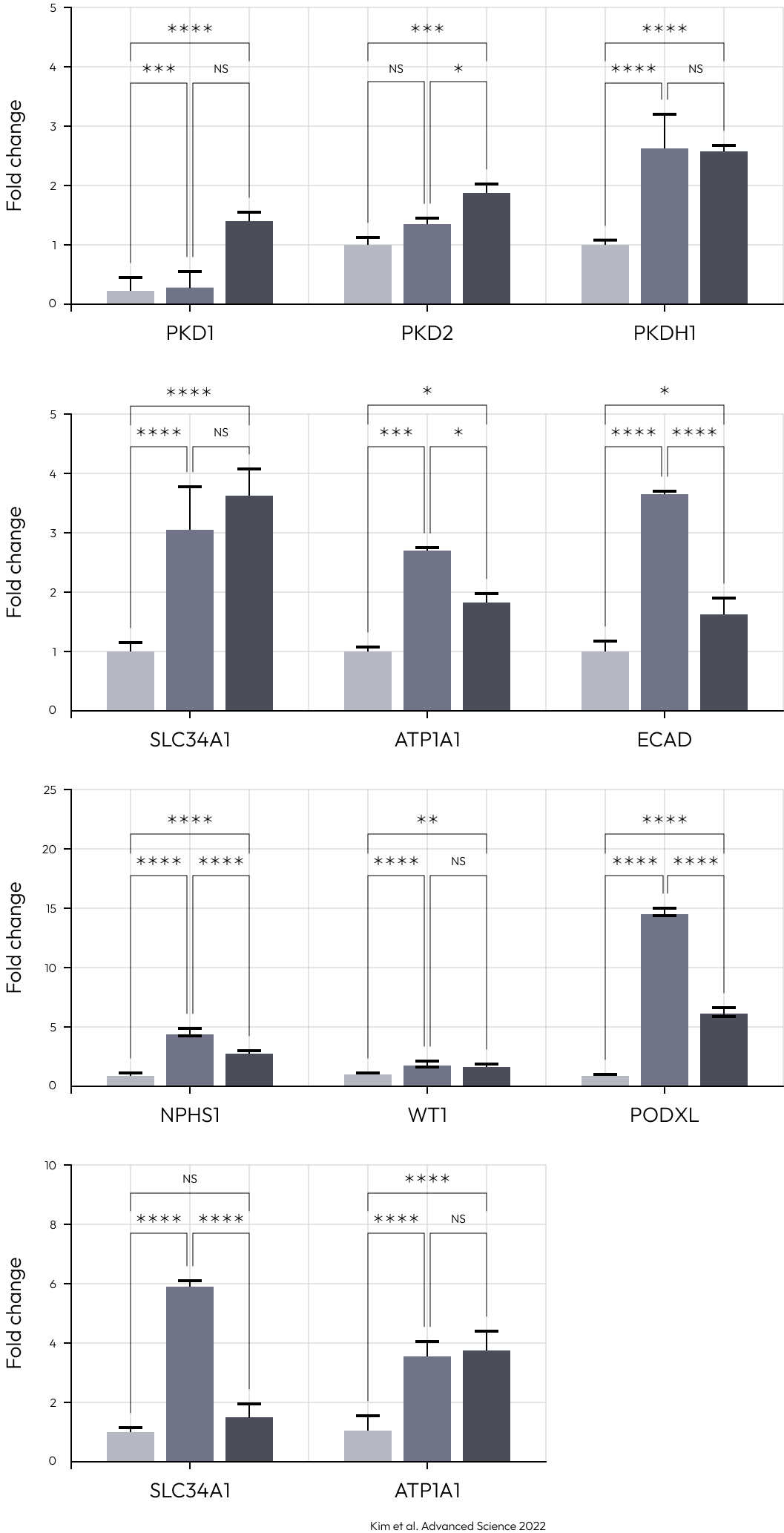
Identifying 18 cell types in kidney organoids through scRNAseq, the research demonstrated improved nephron cell differentiation in the presence of kidney dECM, notably with protocols A and B.
These protocols showed reductions in off-target cells, proliferating cells, and precursor cells.
Pseudo-time ordering further revealed enhanced cell maturity in organoids cultured with protocols A and B.
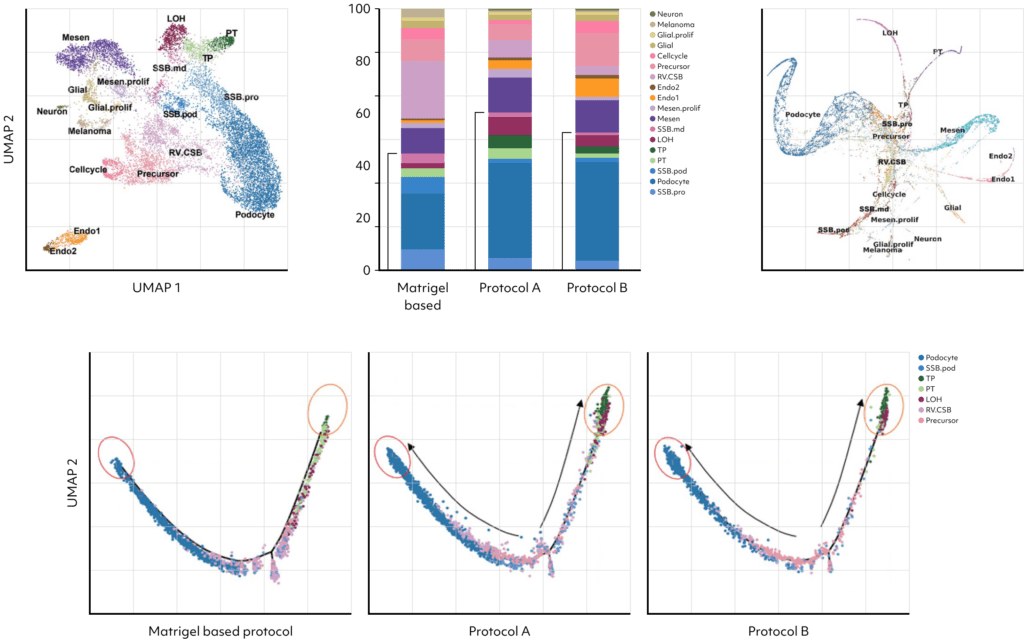
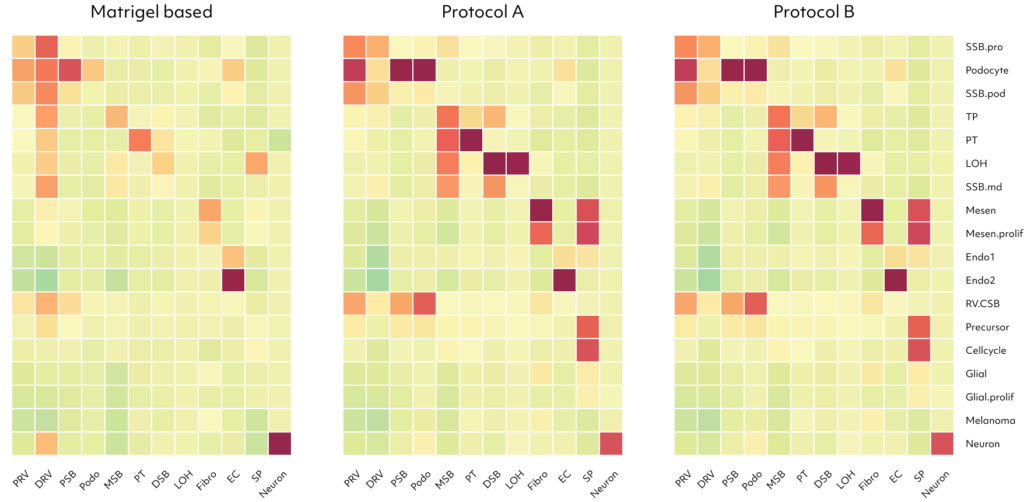
Examining upregulated genes in podocytes generated by protocols A and B, the functional enrichment analysis for Gene Ontology (GO) biological processes revealed their predominant involvement in kidney and nephron development. These findings suggest that kidney dECM influences genes associated with kidney development, enhancing maturation into nephron cells. Notably, podocytes induced by protocols A and B exhibited a high resemblance to human and fetal podocytes and proximal tubule (PSB), while those induced by the Matrigel-based protocol showed lower similarity. Furthermore, various cell types induced by protocols A and B demonstrated increased similarity to human and fetal kidney cell types.
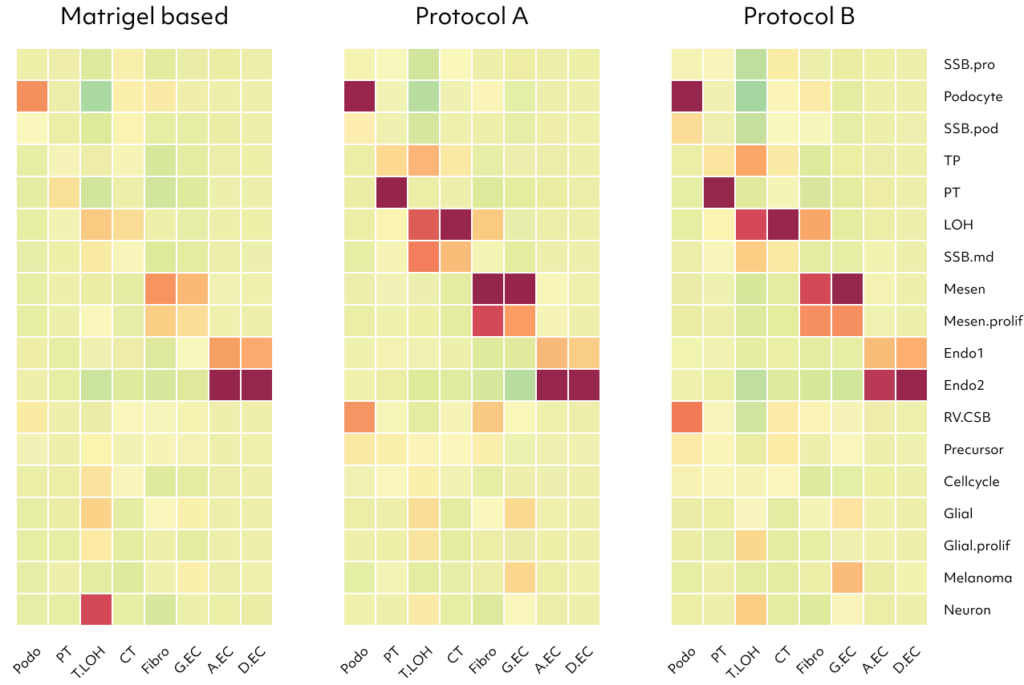
Lambda Biologics GmbH
Deutscher Platz 5 c, 04103, Leipzig, Germany
info@lambdabiologics.com