Price | 5500€+ Login to see price |
Organism | Human |
Product Type | iPS-derived organoid |
Tissue | Liver |
Disease | – |
Applications
-

With the global rise of K-beauty, the cosmetics industry continues to grow steadily. Since the ban on animal testing for cosmetics in Korea in 2017, various alternative testing methods have...

Traditional microscopy methods often require fluorescent labeling to analyze cellular structures, which can be time-consuming and invasive. In contrast, our HT-X1 system allows for high-resolution visualization of cellular morphology without...

Traditional protein analysis has primarily focused on quantifying expression levels within tissue samples. However, recent advances in spatial analysis techniques have shifted attention toward evaluating not only expression levels, but...
Among the many fermented foods we consume, kimchi is particularly known for containing a diverse range of lactic acid bacteria, which are believed to influence the activation of immune cells...
We conducted a study focused on identifying disease-related markers using patient-derived tissue samples. However, traditional methods limited our ability to analyze multiple candidate markers simultaneously, and the limited availability of...
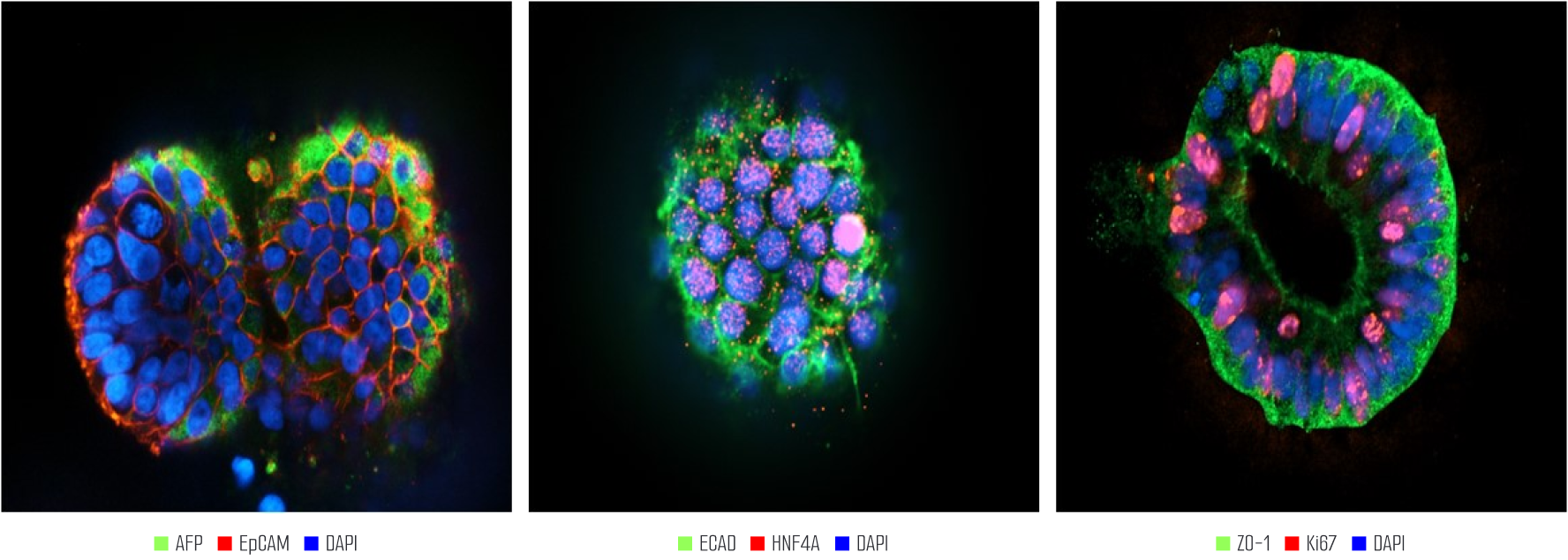
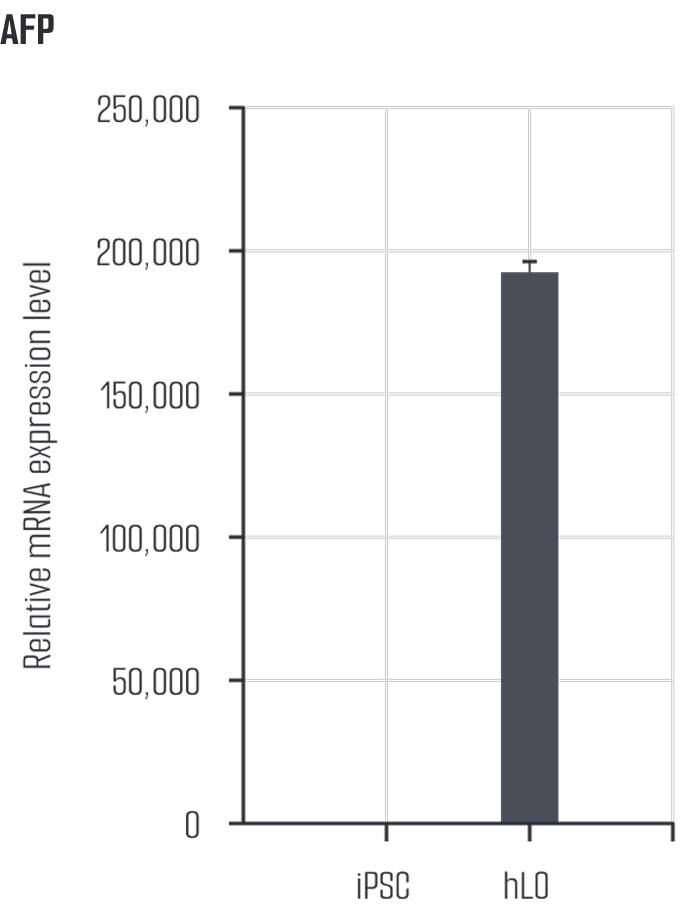
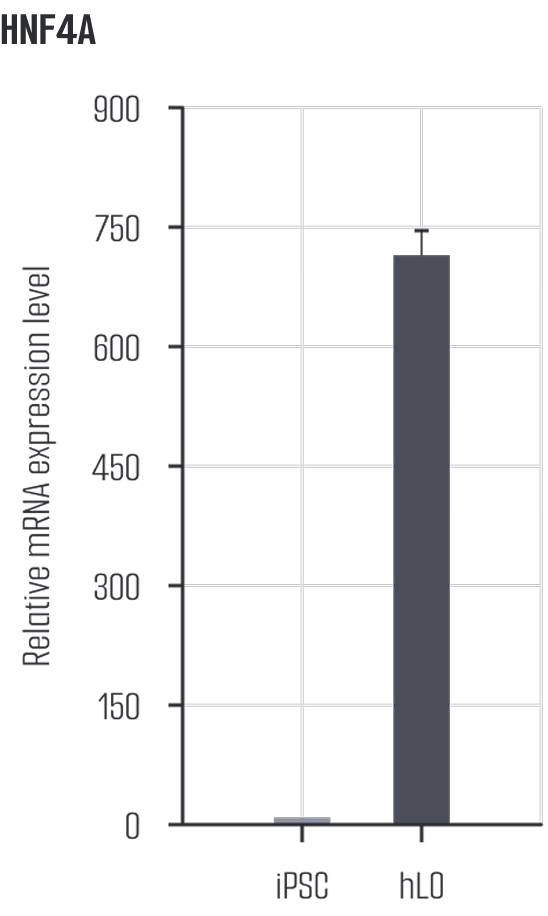
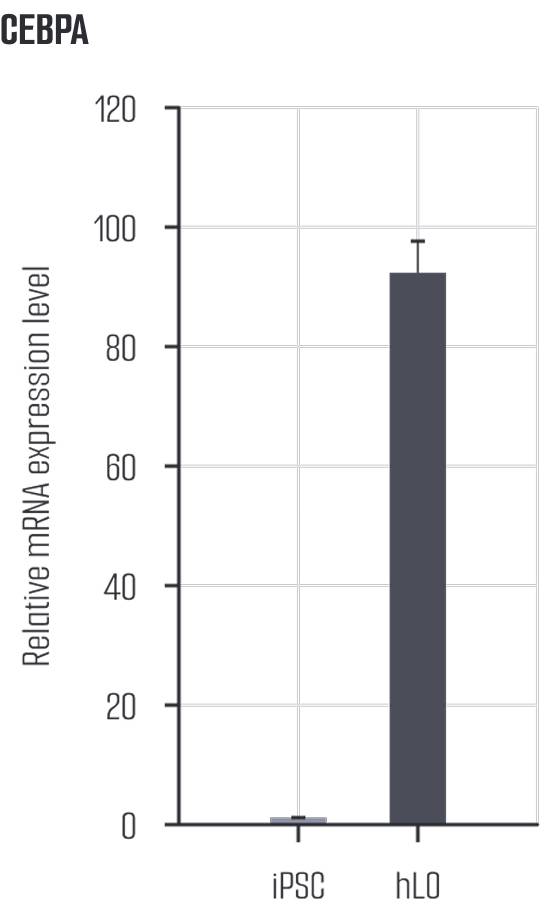
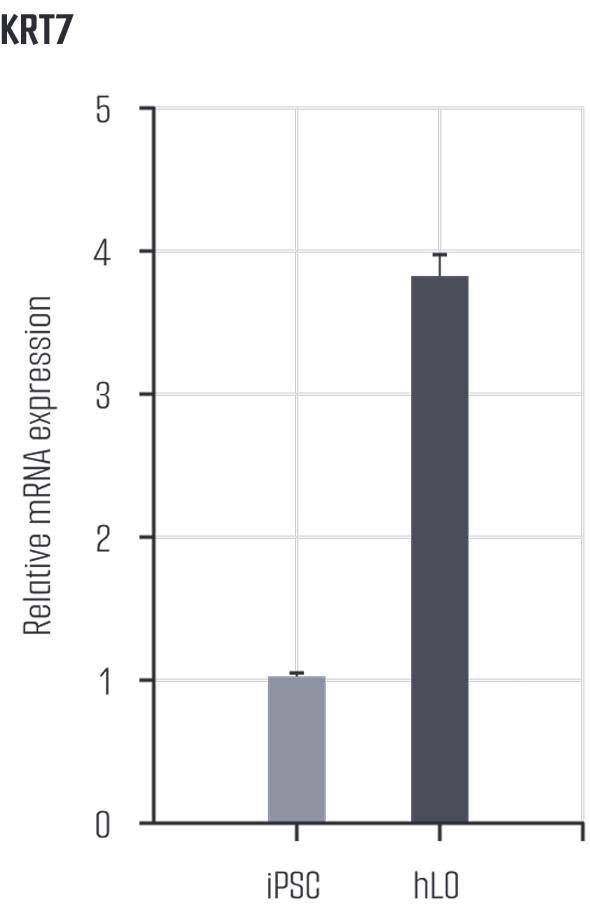
Liver organoids closely resemble human liver tissue, replicating both cell types and functions. EpCAM is expressed in hepatocytes and cholangiocytes, indicating epithelial cell adhesion and structural arrangement, while AFP is expressed in immature hepatocytes, reflecting developmental characteristics. Ki67 marks cell division, appearing in hepatocytes and progenitor cells, and ZO-1 is expressed in hepatocytes and cholangiocytes, assessing barrier function. HNF4A is expressed in hepatocytes and promotes hepatocyte differentiation and maturation, while E-cadherin (ECAD) maintains adhesion between hepatocytes and cholangiocytes, playing a key role in epithelial structure formation. These markers reflect the expression of various cell types in liver organoids, effectively mimicking the complex structure and function of human liver tissue.
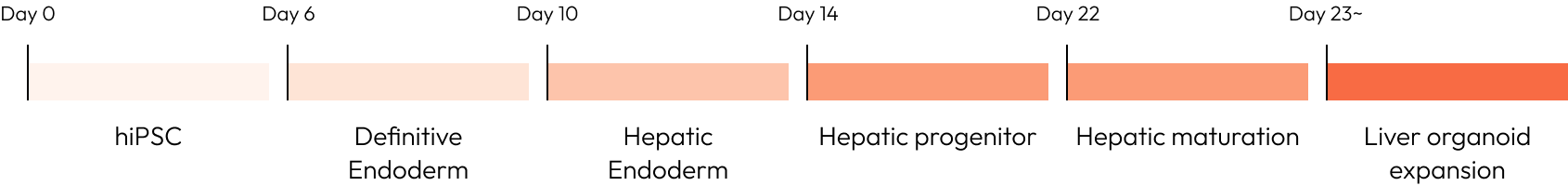
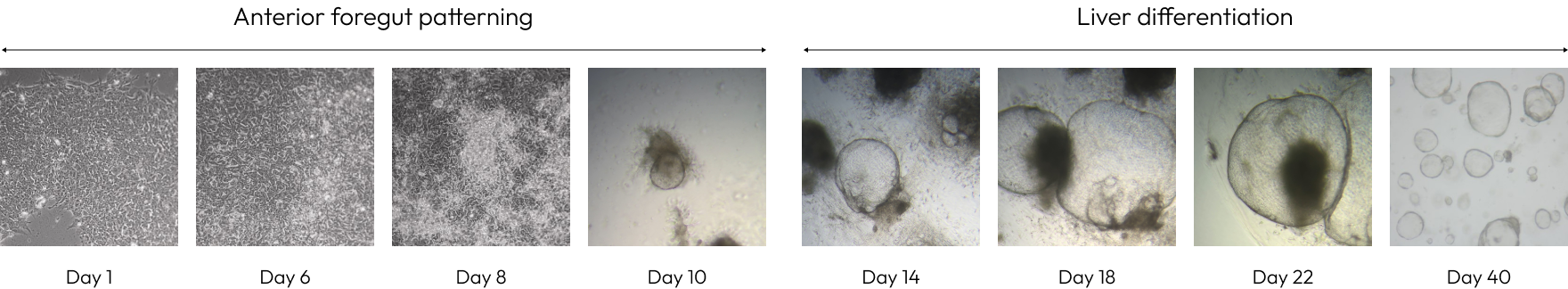
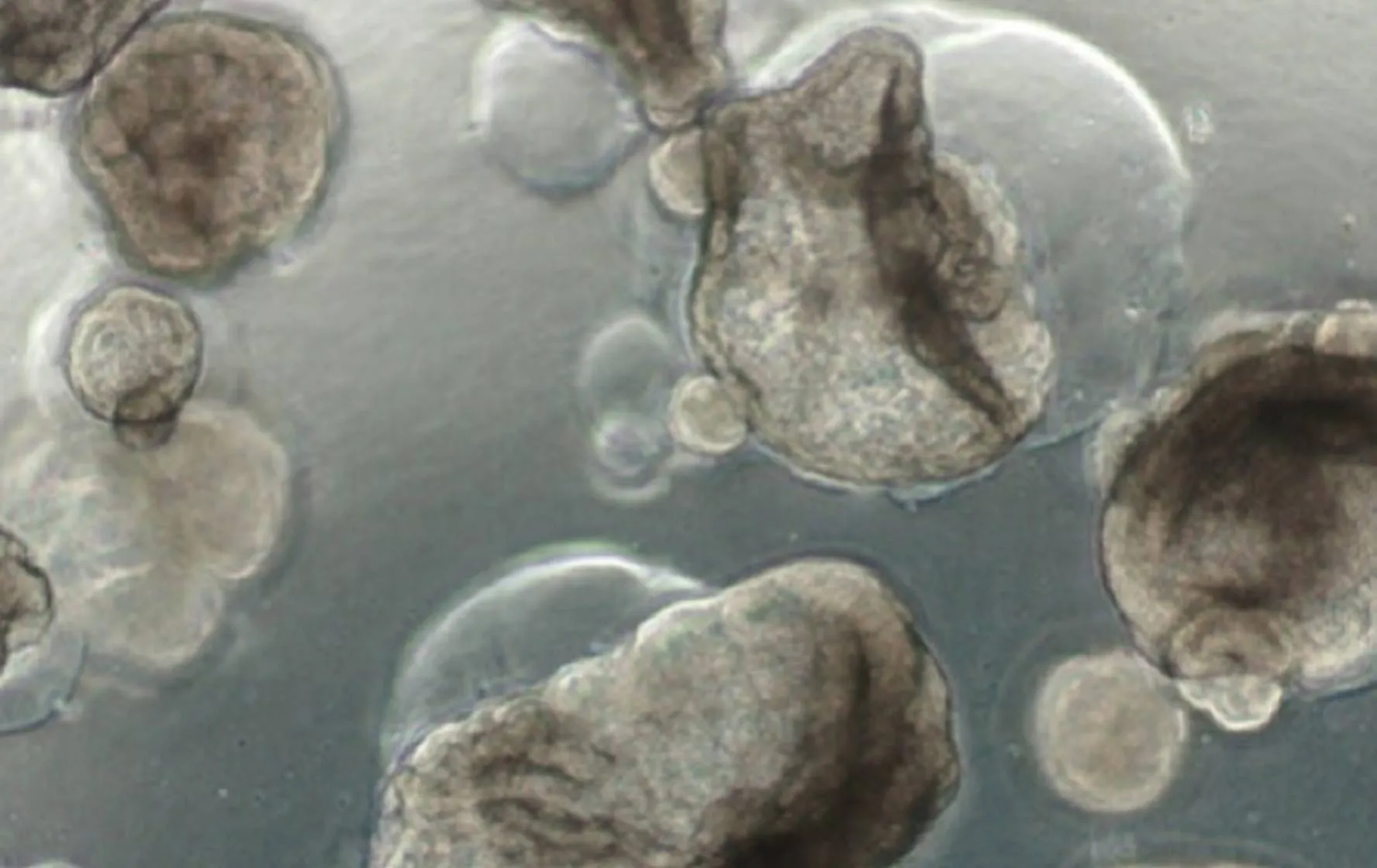
Liver organoids can be observed in a mature form with hepatic layers, bile duct structures architecture similar to actual liver tissue.
They are also composed of various cells such as hepatocytes, cholangiocytes, Kupffer cells, stellate cells.

To induce a fatty liver model, we treated the liver organoids with free fatty acids.
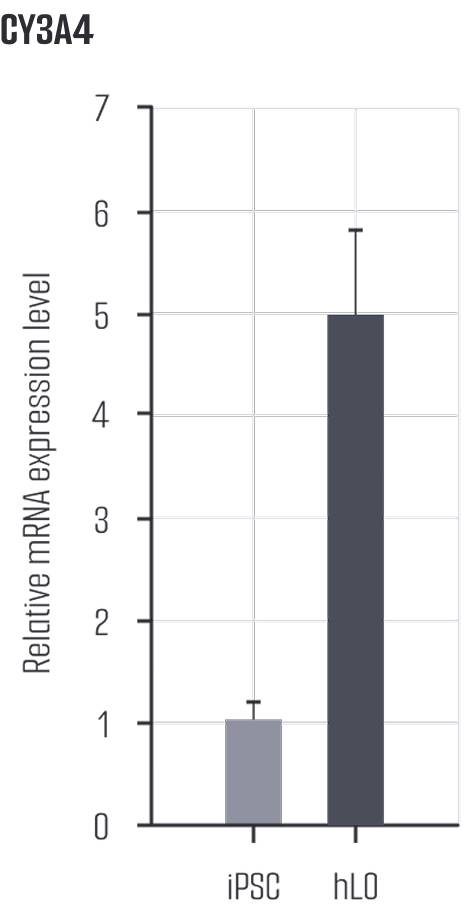
It was confirmed that markers such as HNF4A, Albumin, and CYP3A4, which are indicative of healthy hepatocyte function, decreased in the damaged model.
This model can be used to evaluate effective substances related to fatty liver disease treatment.
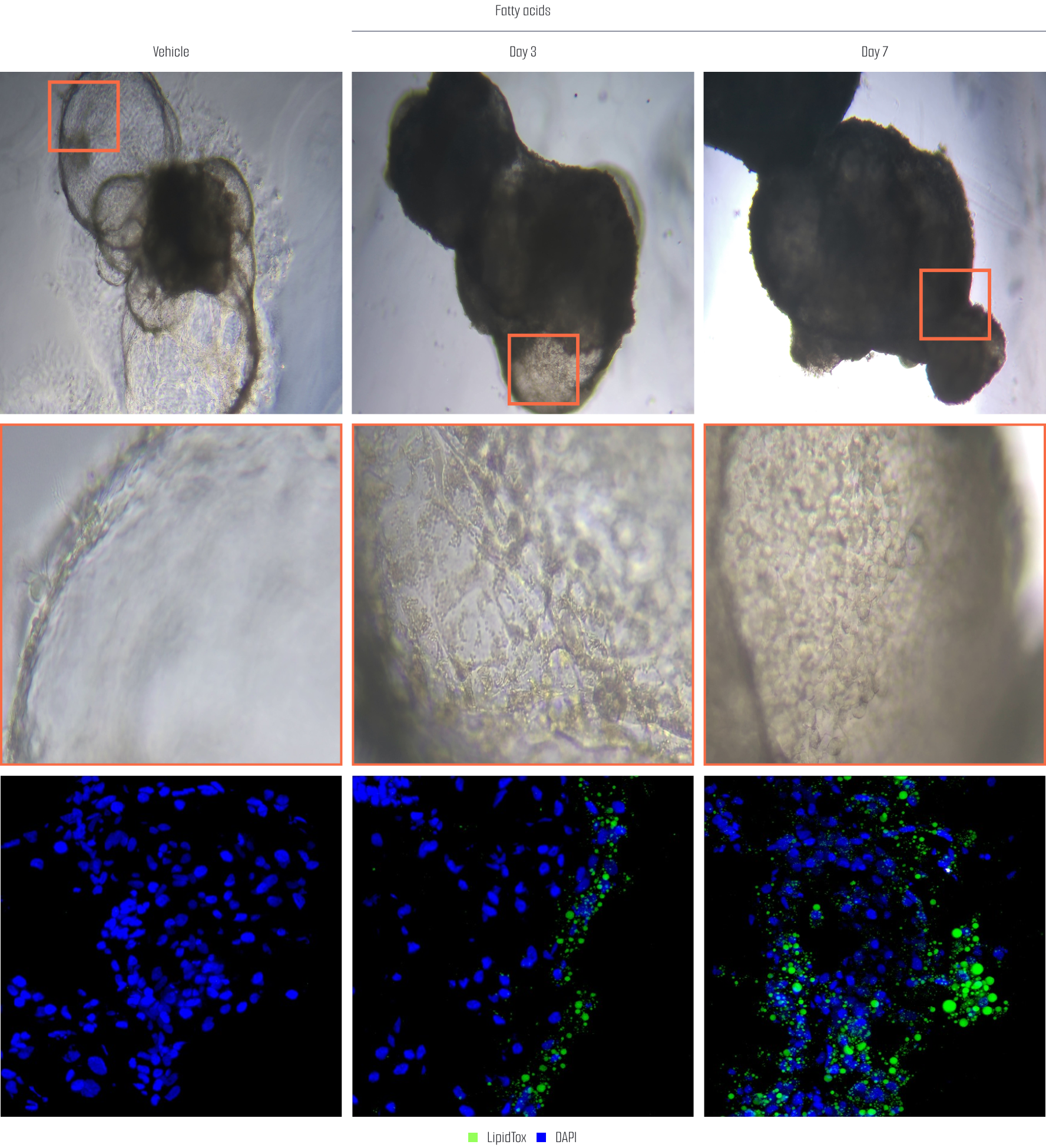
After treating liver organoids with fatty acids, a fatty liver model was created, and lipid accumulation was assessed using LipidTox staining at Day 3 and Day 7. The results showed that at Day 3, lipid accumulation was observed at an early stage, while at Day 7, lipid accumulation was significantly more pronounced. This indicates that, over time, the accumulation of lipids in the liver organoids increases, suggesting that this model effectively simulates the development of fatty liver and can be used as a valid model for research.
Lambda Biologics GmbH
Deutscher Platz 5 c, 04103, Leipzig, Germany
info@lambdabiologics.com