Price | 7500€+ Login to see price |
Organism | Human |
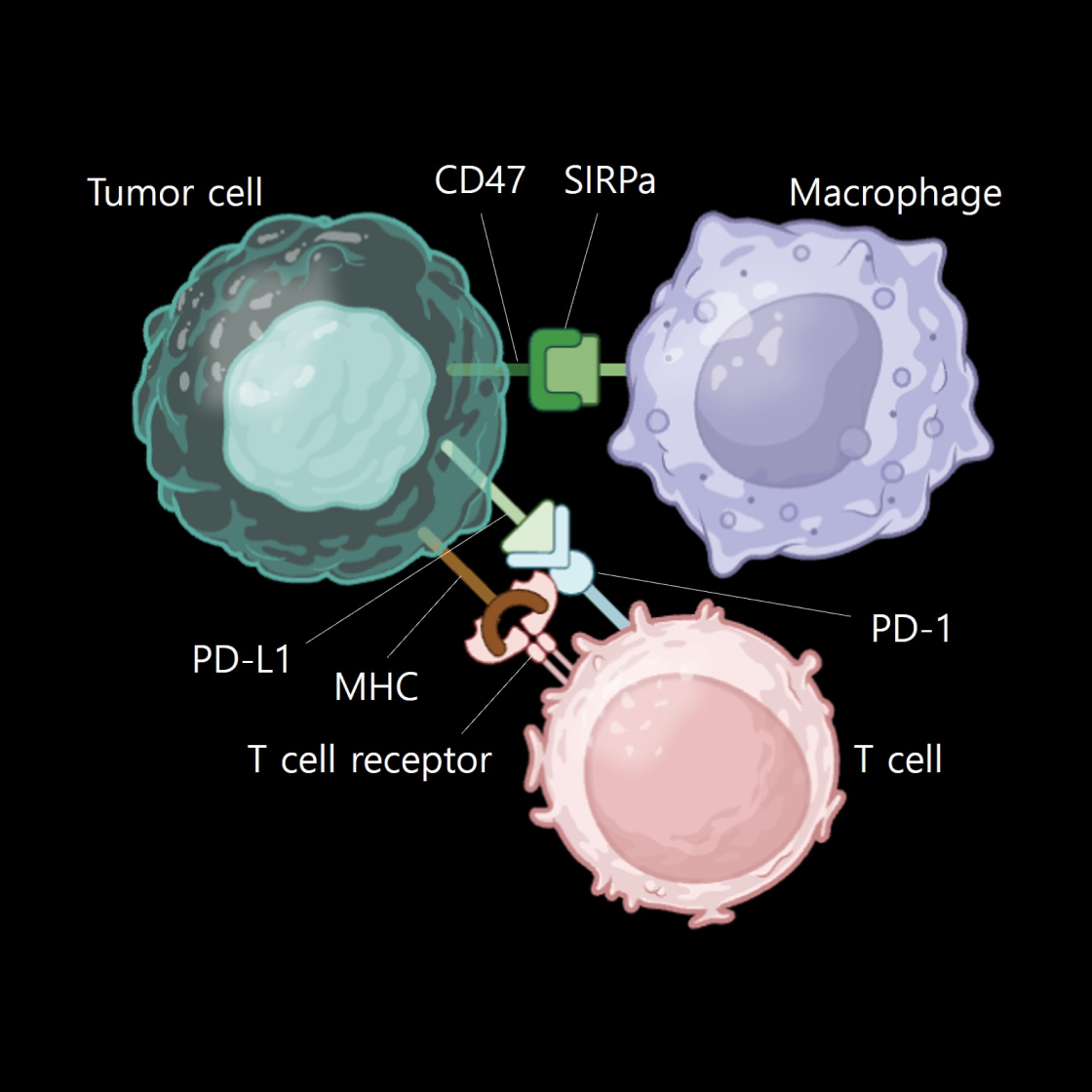
Product Type | Organoid + T cell + Macrophage |
Tissue | Innate |
Disease | – |
Applications
Cancer Organoid
Colorectal Cancer
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Pancreatic Cancer
Breast Cancer
Cholangiocarcinoma
Gastric Cancer
Ovarian Cancer

With the global rise of K-beauty, the cosmetics industry continues to grow steadily. Since the ban on animal testing for cosmetics in Korea in 2017, various alternative testing methods have...

Traditional microscopy methods often require fluorescent labeling to analyze cellular structures, which can be time-consuming and invasive. In contrast, our HT-X1 system allows for high-resolution visualization of cellular morphology without...

Traditional protein analysis has primarily focused on quantifying expression levels within tissue samples. However, recent advances in spatial analysis techniques have shifted attention toward evaluating not only expression levels, but...
Among the many fermented foods we consume, kimchi is particularly known for containing a diverse range of lactic acid bacteria, which are believed to influence the activation of immune cells...
We conducted a study focused on identifying disease-related markers using patient-derived tissue samples. However, traditional methods limited our ability to analyze multiple candidate markers simultaneously, and the limited availability of...
Lambda Biologics GmbH
Deutscher Platz 5 c, 04103, Leipzig, Germany
info@lambdabiologics.com