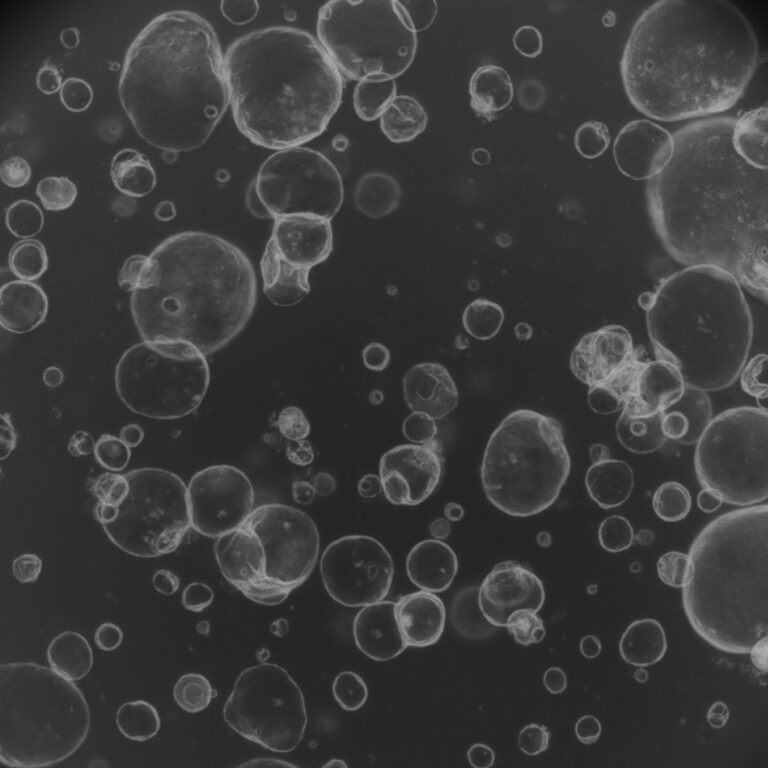
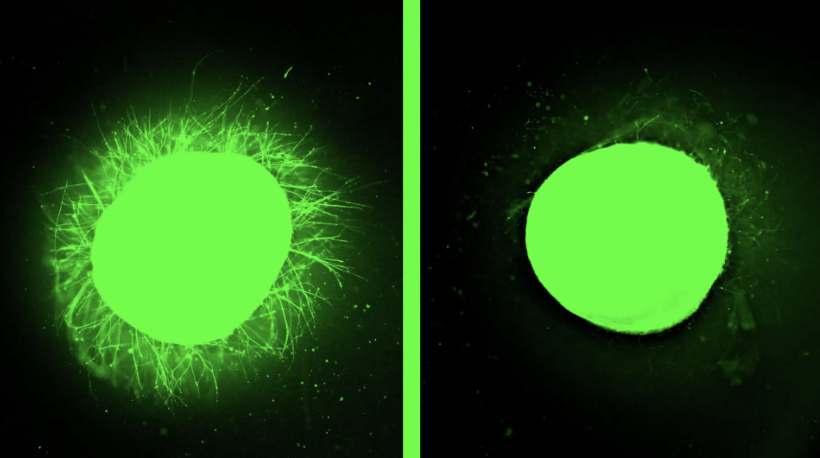
AI-Enhanced OC-PAM Enables Advanced 3D Imaging of Cancer Organoids and Spheroids
Journal: Light: Science & Applications
Author: Deloria, A.J., Csiszar, A., Deng, S. et al., Austria
This study presents a multimodal optical coherence photoacoustic microscopy (OC-PAM) system that enables label-free, high-resolution 3D imaging of cancer organoids and spheroids, overcoming common limitations of conventional optical techniques. Combined with AI-based segmentation and radiomics analysis, the platform allows automated tracking of organoid viability and precise mapping of melanin-positive cells within heterogeneous tumor models.
Abasic crRNAs Improve CRISPR–Cas9 Specificity by Reducing Off-Target Effects
Journal: Nature Chemical Biology
Author: Gu, D., Kim, GW.D., Park, M. et al., Korea
This study reveals that naturally occurring abasic modifications at the 5′ end of CRISPR RNAs in Streptococcus pyogenes reduce off-target DNA cleavage while preserving on-target editing efficiency. Inspired by this mechanism, the authors engineered abasic-modified guide RNAs that enhance SpCas9 fidelity beyond existing variants, offering a promising strategy for more precise genome editing in vivo.
spEMO Integrates Histopathology and Spatial Multi-Omics Through Multi-Modal AI
Journal: Nature Biomedical Engineering
Author: Liu, T., Huang, T., Ding, T. et al., USA
This study introduces spEMO, a computational framework that integrates pathology foundation models with large language model embeddings to jointly analyze histopathology and spatial multi-omic data. By leveraging multi-modal representations, spEMO outperforms single-modality approaches across tasks such as spatial domain identification, disease prediction, multicellular interaction inference, and automated medical reporting, advancing interpretable AI for spatial biology and clinical applications.
Enabling Continuous Passaging of Human Norovirus in Intestinal Enteroids
Journal: Science Advances
Author: Gurpreet Kaur et al. ,
This study identifies host chemokines (CXCL10, CXCL11, and CCL5) as restriction factors limiting human norovirus replication in human intestinal enteroids (HIEs) and demonstrates that the antagonist TAK-779 enhances viral replication and spread. The approach enables continuous passaging of GII.3 norovirus and generation of viral stocks, providing a scalable in vitro system to advance studies of norovirus biology, strain-specific host interactions, and therapeutic development.