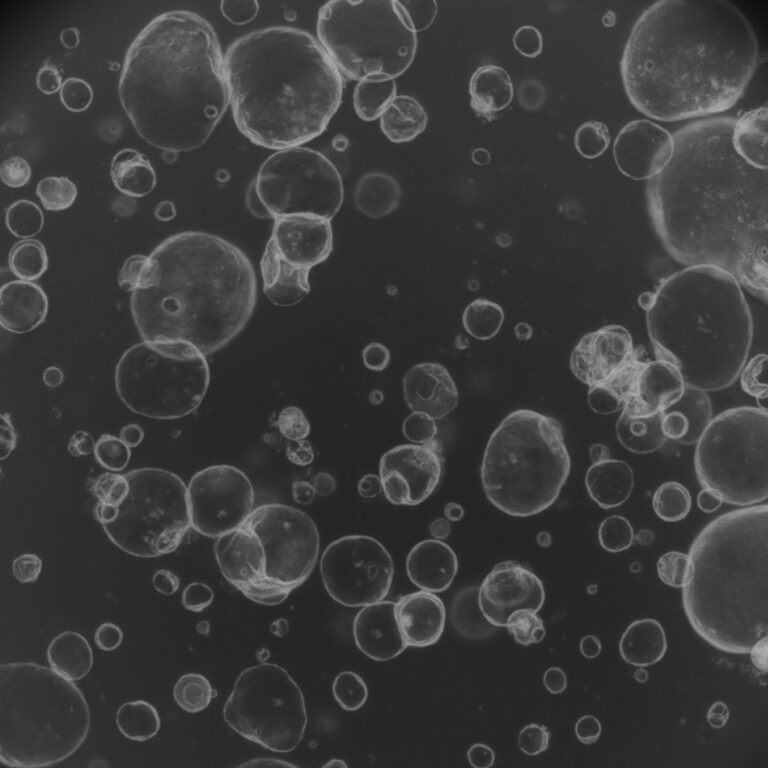
Placenta-derived factors contribute to human iPSC-liver organoid growth
Journal: Nature Communications
Author: Yoshiki Kuse et al., Japan
The study illustrates that mimicking the natural hypoxic environment and adding placenta-derived IL1α enhanced liver organoid growth from human iPSCs by boosting progenitor cell expansion, later improved by oxygenation.
Vascular network-inspired diffusible scaffolds for engineering functional midbrain organoids
Journal: Cell – Stem Cell
Author: Hongwei Cai et al., USA
Researchers developed 3D-printed tubular channel networks (VID scaffolds) to enhance oxygen and nutrient delivery in organoids. These scaffolds eliminated necrosis in midbrain organoids, improving their development, maturation, and neural activity. The engineered organoids better model drug responses, advancing organoid research for developmental biology and therapeutics.
Shaping early neural development by timed elevated tissue oxygen tension: Insights from multiomic analysis on human cerebral organoids
Journal: Science Advances
Author: Yuan-Hsuan Liu et al., Taiwan
Scientist discovered a critical 4-6 week period of elevated oxygen tension in cerebral organoids that drives neurogenesis. Neuroglobin gene plays a key role, as its silencing reduces oxygen levels and impairs neural development.
Simultaneous CRISPR screening and spatial transcriptomics reveal intracellular, intercellular, and functional transcriptional circuits
Journal: Cell
Author: Loϊc Binan et al., USA
Perturb-FISH combines CRISPR screening with spatial transcriptomics to analyze both intracellular and intercellular genetic effects at single-cell resolution, enabling studies of cell density-dependent interactions and linking genetic perturbations to functional phenotypes.