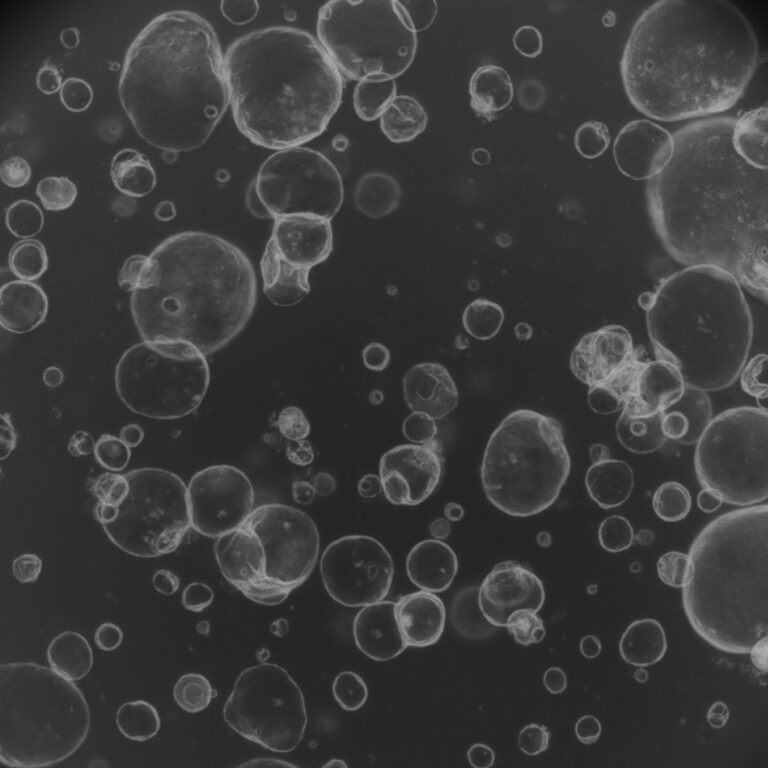
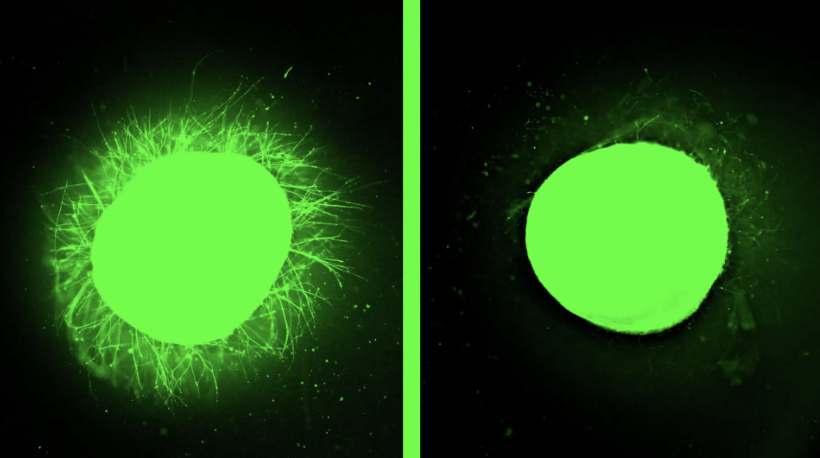
Mitochondrial fusion and cristae reorganization facilitate acquisition of cardiomyocyte identity during reprogramming of murine fibroblasts
Journal: Cell Reports
Author: Brian M. Spurlock et al., USA
This study reveals that mitochondrial fusion is essential for converting cardiac fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes (iCMs), while fission inhibits this process. Specifically, silencing Mtfr1l, a mitochondrial fission regulator, significantly enhanced iCM conversion and maturation by promoting fusion, mitochondrial respiration, and cristae reorganization.
Identifying perturbations that boost T-cell infiltration into tumours via counterfactual learning of their spatial proteomic profiles
Journal: Nature Biomedical Engineering
Author: Zitong Jerry Wang et al., USA
The researchers introduce Morpheus, a deep learning model that analyzes spatial proteomic tumor data to predict T-cell infiltration and identify minimal molecular perturbations to enhance it. Applied to melanoma and colorectal cancer samples, it discovered cancer-specific combinatorial therapies that were validated through in vitro experiments.
Aspirin prevents metastasis by limiting platelet TXA2 suppression of T cell immunity
Journal: Nature
Author: Jie Yang et al., UK
Scientists discovered aspirin enhances anti-cancer immunity by blocking platelet-derived thromboxane A2 (TXA2), which suppresses T-cells through ARHGEF1. This mechanism explains aspirin’s ability to reduce metastasis, opening possibilities for more targeted cancer prevention therapies with fewer side effects.
Spatial Transcriptomics Delineates Potential Differences in Intestinal Phenotypes of Cardiac and Classical Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Journal: iScience
Author: Kathryn Y. Burge et al., USA
This study used spatial transcriptomics to compare two forms of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). Classical NEC shows dysbiosis-induced inflammation and metabolic acidosis, while cardiac NEC (in infants with heart disease) features reduced angiogenesis and ER stress-induced apoptosis, suggesting distinct pathophysiological mechanisms despite similar clinical presentations.