Melbourne Researchers Open Possibility for Customized Leukemia Treatment with iPSC-Derived Blood Stem Cells
Journal: Nature Biotechnology
Author: Elizabeth S. Ng, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, Australia
Summary: Melbourne researchers have developed blood stem cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells, opening up possibilities for personalized leukemia and bone marrow transplant treatments.
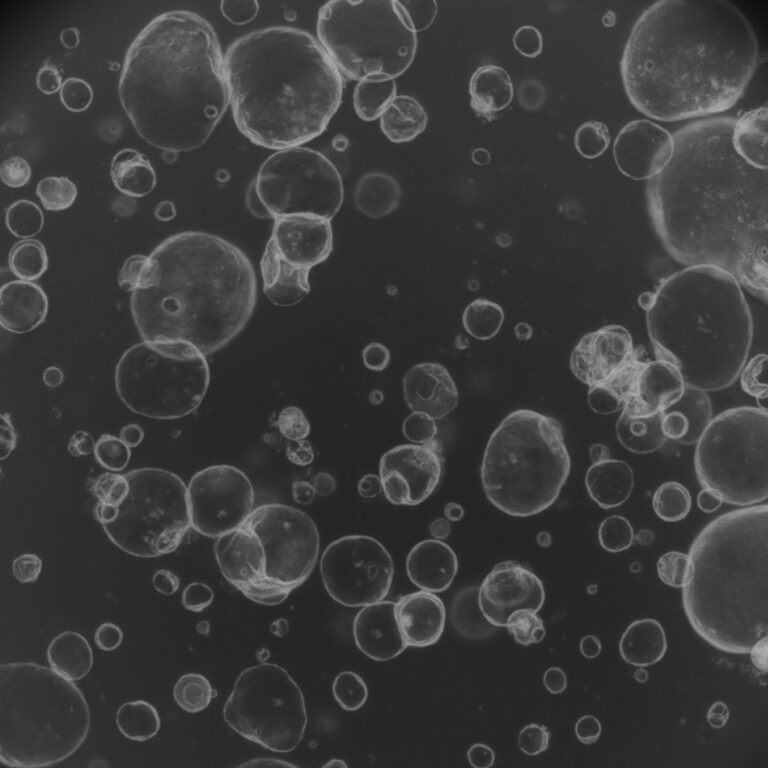
Researchers at the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) in Melbourne have successfully developed blood stem cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), paving the way for personalized leukemia and bone marrow transplant treatments. This study confirmed that lab-produced blood stem cells show characteristics similar to those of actual human embryonic blood stem cells, verifying their potential for clinical application. This discovery represents a significant advancement in developing customized treatments for childhood leukemia and bone marrow failure disorders.
Development of an Innovative Tool for Non-Invasive Delivery of CRISPR-Cas9
Journal: Development
Author: Zak Swartz, Marine Biological Laboratory, USA
Summary: Researchers have developed a new tool called VitelloTag for non-invasive CRISPR-Cas9 delivery, enabling easier transfer of gene editing tools into embryo and egg cells.
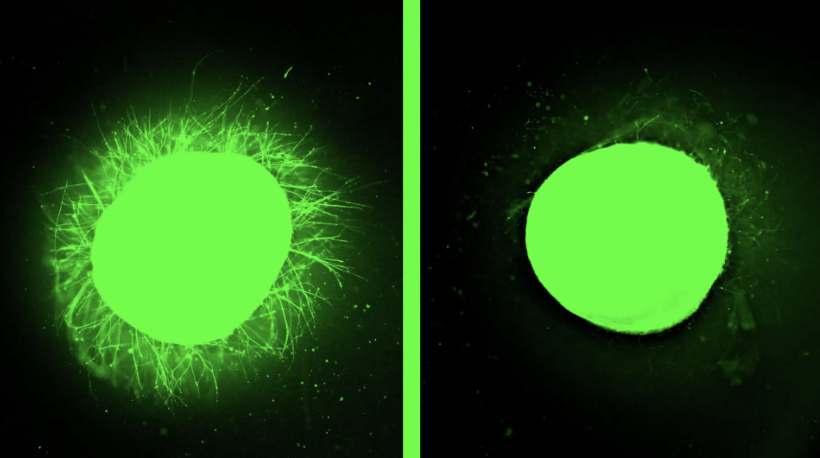
Researchers at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) have developed VitelloTag, a new non-invasive method for easily delivering the gene editing tool CRISPR-Cas9 into egg and embryo cells. VitelloTag utilizes the properties of natural egg proteins to deliver gene editing tools in bulk into cells. This technology is simpler than microinjection methods and can be particularly useful for species that are difficult to inject. The research has been successfully applied to starfish and acorn worms.
One Drug, Multiple Targets: DMLs Strategy for Alzheimer’s Treatment
Journal: Trends in Pharmacological Sciences
Author: Bengisu Turgutalp New York,Columbia University Irving Medical Center NY, USA
Summary: Multi-target drugs (DMLs) that simultaneously target the complex pathological mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease are gaining attention as a new treatment strategy.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has complex, multiple pathological mechanisms, rendering existing single-target therapies ineffective. Multi-target ligands (DMLs) are being researched as a new treatment strategy with the potential to synergistically target various pathological mechanisms of AD simultaneously. Innovations in genetics and pharmacology are enabling the design of these multi-target drugs, and they have a high potential for success as disease-modifying therapies.
Evolving Cartilage Regeneration Technology: Hope for Inflammatory Joint Disease Treatment
Journal: Nature Reviews Rheumatology
Author: Rachel C. Nordberg, University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA, USA
Summary: Recent advances in cartilage tissue engineering are enabling the development of new therapeutic products, making significant progress in treating inflammatory joint diseases, particularly by enhancing immune modulation and mechanical strength.
While cartilage tissue engineering is currently limited in treating non-knee joints, severe osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis, it is developing cartilage with strong mechanical properties through scaffold-based and scaffold-free approaches. The use of immunomodulatory biomaterials and synthetic biology is increasing the likelihood of successful implantation in inflammatory environments. Research focusing on improving the consistency of allogeneic cell sources using tissue banks in animal studies and clinical development is gaining attention.