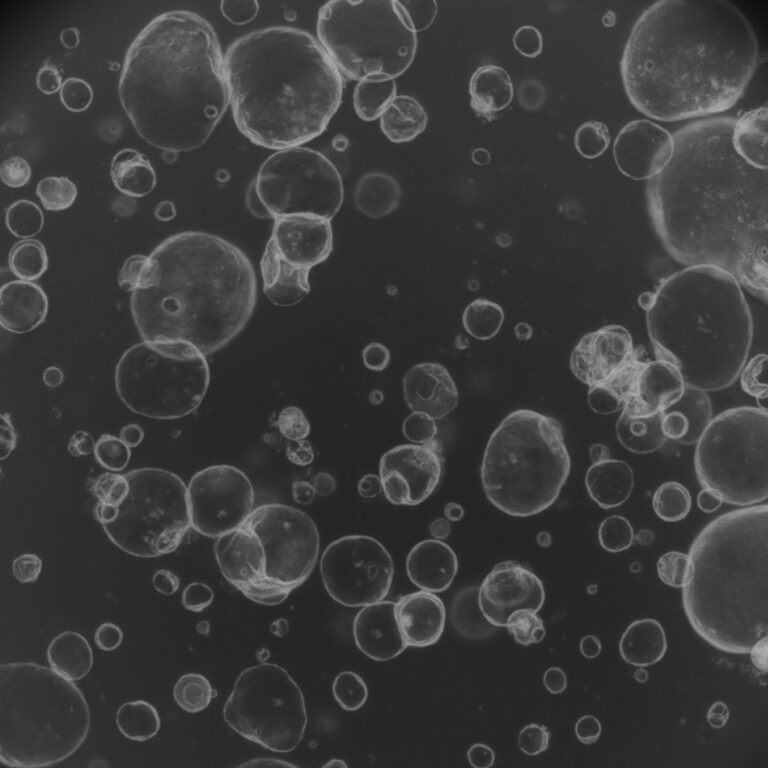
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a challenging disease due to its aggressive nature and complex biology, necessitating effective therapeutic strategies. Pre-clinical models using PDAC organoids combined with real-time monitoring are essential for assessing therapy response. Researchers developed stable live-imaging organoid/peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) co-cultures and introduced OrganoIDNet, a deep-learning algorithm, to analyze bright-field images of murine and human PDAC organoids.
The study assessed the response of PDAC organoids to the chemotherapy drug gemcitabine and the PD-L1 inhibitor Atezolizumab, with and without HLA-matched PBMCs over time. OrganoIDNet’s results were validated using the CellTiter-Glo proliferation assay. Live cell imaging with OrganoIDNet effectively detected size-specific drug responses, revealing that larger organoids were more susceptible to gemcitabine’s cytotoxic effects. This method also differentiated between healthy and unhealthy organoids and measured their eccentricity as a reaction to therapy.
Additionally, the imaging of organoid/PBMCs sandwich-based co-cultures allowed for the longitudinal analysis of organoid responses to Atezolizumab, demonstrating increased PBMCs tumor-killing potency in the presence of the drug. This approach provides a platform for accurately detecting organoid responses to standard PDAC chemotherapy over time and offers dynamic insights into immunotherapeutic effects in individual patient-derived PDAC organoids, promising real-time assessment of immunotherapy effects.
Keywords: organoids, pancreatic cancer, AI