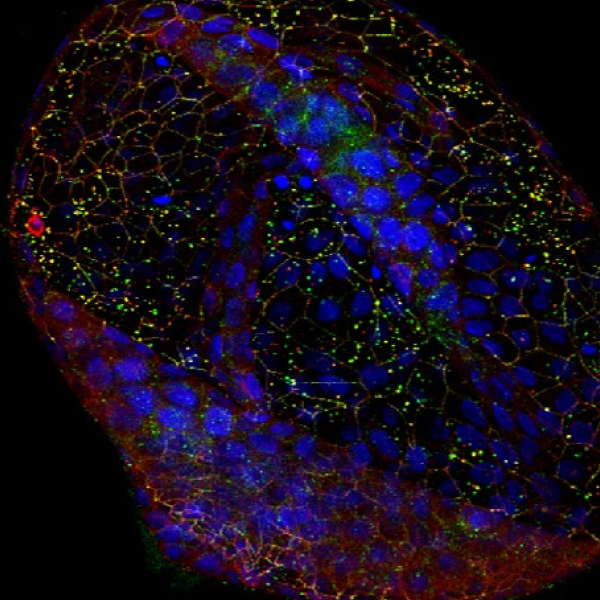
A more accurate assessment and monitoring of the efficacy of the microbiome can be achieved with an organoid model closely resembling the human intestine.

Microbiome
Lambda offers highly human-mimicking intestinal organoids, enabling realistic research not only for long-term studies of the gastrointestinal system but also for more lifelike investigations into the interactions between cells and microorganisms.
This platform is versatile, serving as a valuable tool for drug development and disease research.
Cell Type
· ASC
Organoid type
· Intestinal organoid
Lambda provides a 2D platform for gut attachment and allows for the evaluation of probiotics efficacy through gut attachment analysis.
Cell Type
· iPSC
Organoid type
· Intestinal organoid
Probiotics, known to exist in the gut, must possess the ability to survive in the body and exhibit high attachment capabilities to colon epithelial cells to exert various physiological functions in the human system.
Lambda provides a 2D platform for gut attachment and allows for the evaluation of probiotics efficacy through gut attachment analysis.
Production of beneficial substances
Metabolites with efficacy are produced.
Acid resistance, Bile resistance
Must survive to reach the intestine.
Intestinal colonization
Must attach to intestinal epithelial cells and colonize.
Discover the intricacies of intestinal colonization: Dive deeper into understanding the crucial role of microbial inhabitants in your gut health.
Key to successful probiotic formulation development: Gut colonization.
Caco-2 cell
Functional hIEC
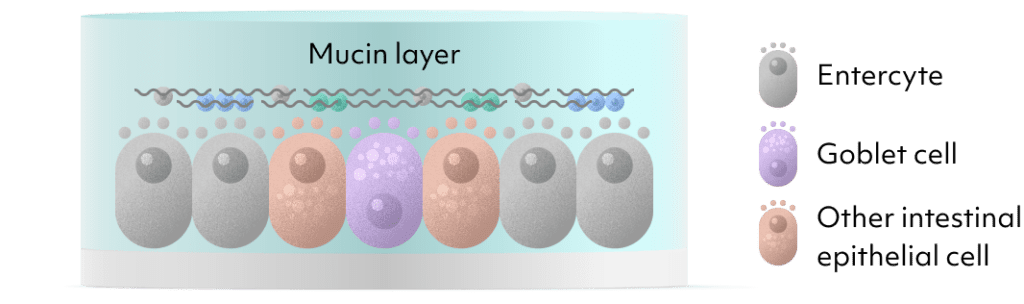
Introducing our state-of-the-art Human Intestinal Epithelial Cell (hIEC) model, a significant advancement over traditional colorectal cancer cell models like Caco-2.
This innovative model replicates the diverse cell types found in the human intestine,
including enterocytes and goblet cells, creating a Mucus Layer remarkably similar to that in the human body.
This model exhibits a significant increase in mucin-related gene expression, critical for intestinal mucosa, underscoring
its immense potential as a key tool in gut health research and pharmaceutical development.
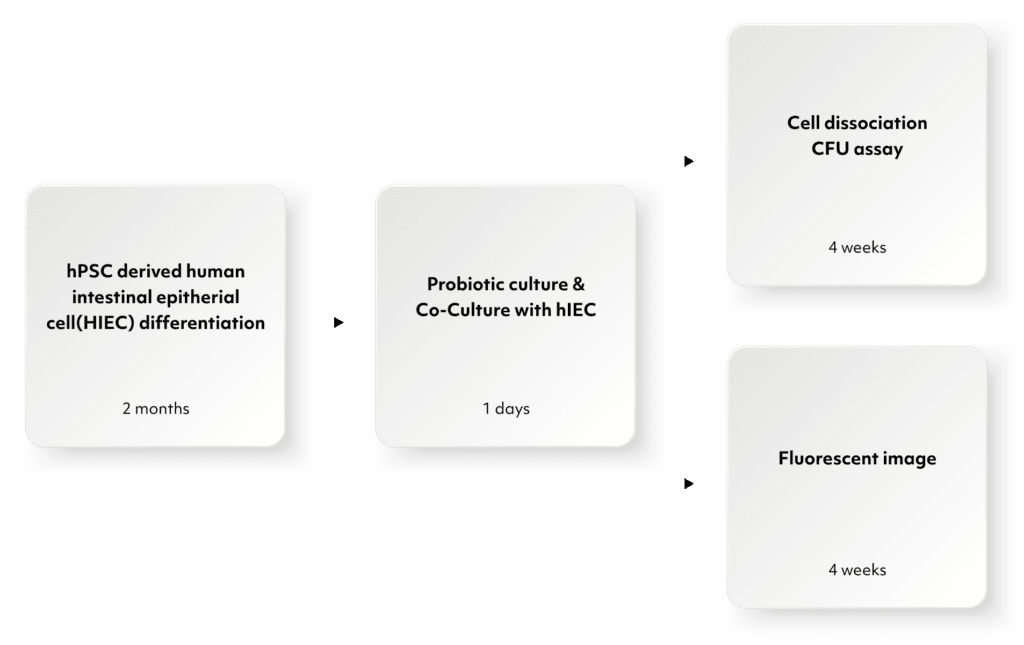
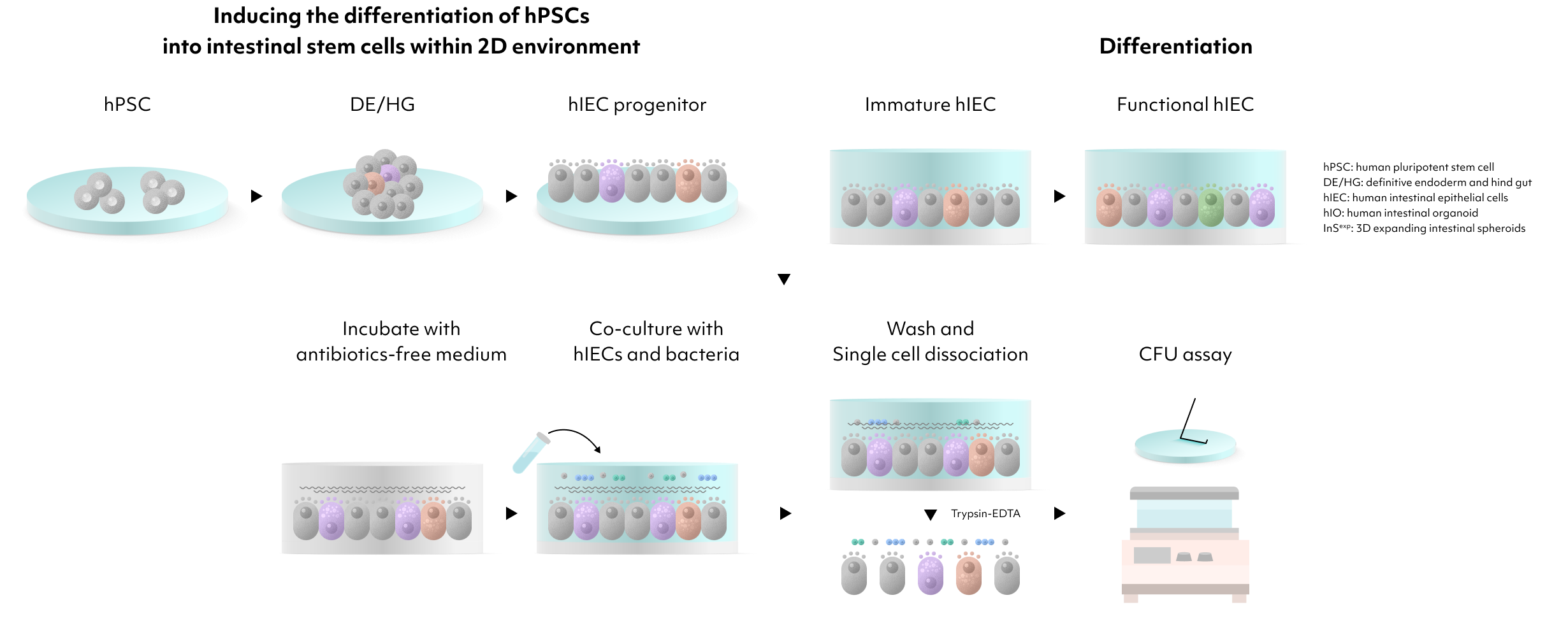
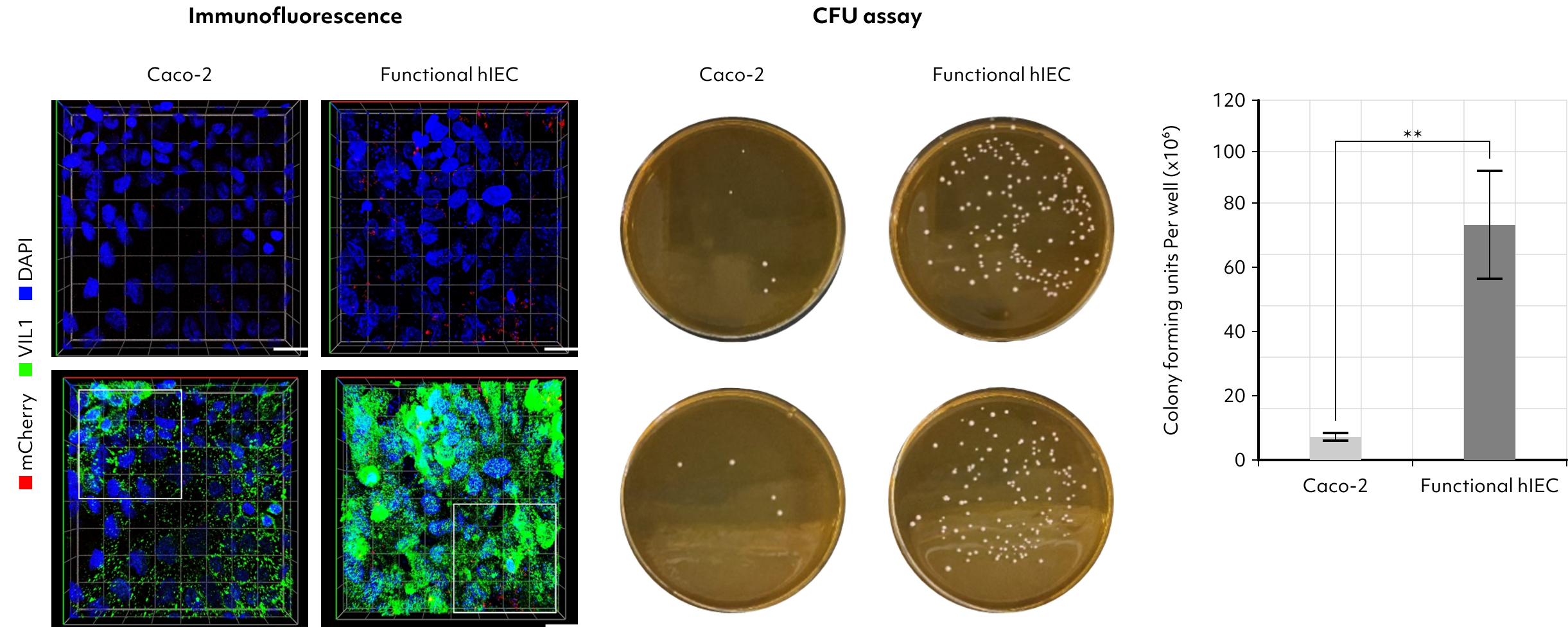
hIEC model is anticipated to play a crucial role in various fields, including drug development, gut health research, and disease modeling.
Utilizing this model, we have assessed drug absorption and permeability, and analyzed metabolites, yielding results more closely aligned with clinical data than those obtained with the traditional Caco-2 cell model.