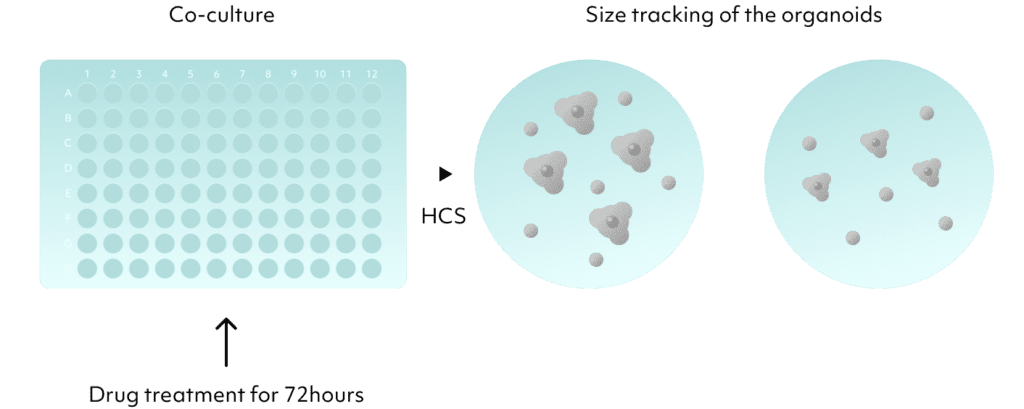
A co-culturing platform of macrophages and organoids demonstrates varying organoid cytotoxic effects depending on the ratio of M1 macrophages to M2 macrophages.
Optimal cell death effects are established by co-culturing different ratios of functionally diverse immune cells.
This enables the identification of optimal conditions for co-culturing various immune cells, facilitating the selection of an appropriate platform for drug testing.

Macrophage
Colorectal cancer organoids accurately replicate the complexities of patient tumors, including heterogeneity,
genetic traits, and tissue structure.
These organoids serve as a versatile platform for drug testing, allowing the evaluation of drug responses and sensitivity.
Additionally, they facilitate personalized disease modeling using patient-specific samples, contributing to biomarker identification for prognosis and treatment response.
NSCLC organoids, reflecting the heterogeneity and genetic features of patient tumors, provide a versatile platform for in-depth cancer research.
These organoids faithfully mimic the tissue architecture of NSCLC, facilitating the study of tumor dynamics, invasion patterns, and drug responses.
Their patient-specific modeling capability allows personalized exploration of treatment outcomes.
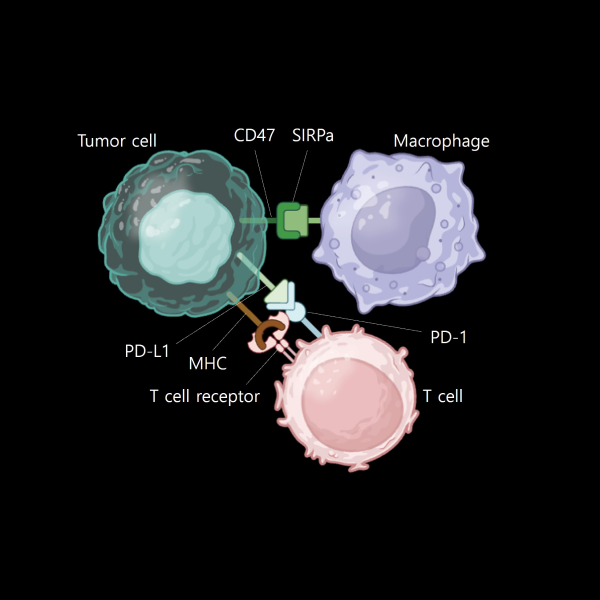
The co-culture drug evaluation solution with macrophages, T cells, and cancer organoids allows for the simultaneous observation of the phagocytic activity of macrophages and the cytotoxic ability of T cells.
Co-culturing with both M1 and M2 macrophages is possible, mimicking the role of macrophages observed in actual cancer tissues.