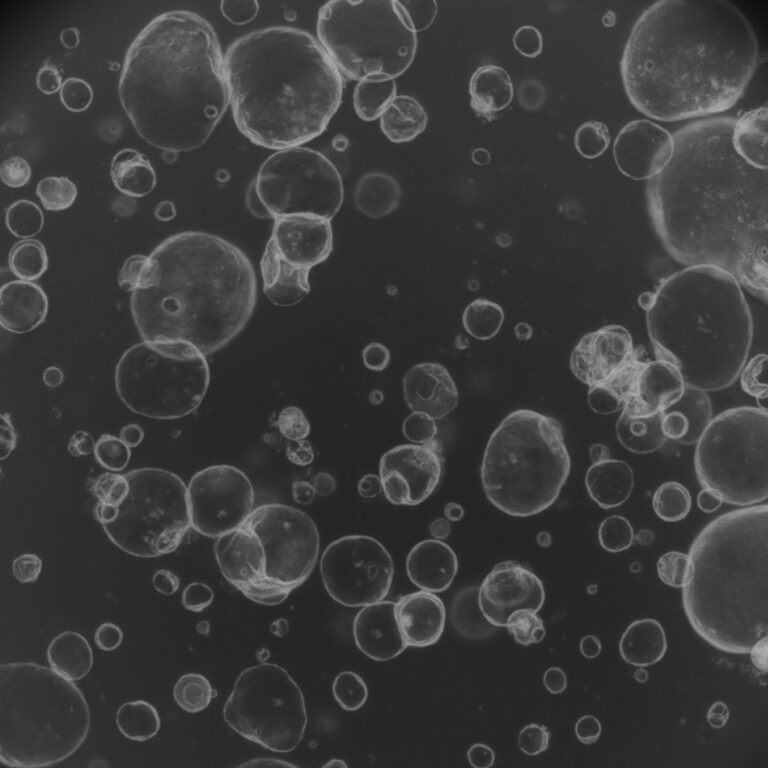
Drug-induced bile duct injury is a common issue in clinical practice, presenting various pathological features. Although several drugs have been implicated in bile duct damage, the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. This study introduces an in vitro model using CLCOs (cholangiocyte-like cells) to simulate bile duct injury. The results demonstrate that CPZ (chlorpromazine) induces dose- and time-dependent damage to CLCOs, particularly under cholestatic conditions. CPZ alone does not trigger inflammation, but in combination with TNFα, an inflammatory response is observed. Additionally, CPZ induces oxidative stress and inhibits the expression of efflux transporters, suggesting a potential mechanism for cholestasis induction. This model could be valuable for preclinical safety assessments to predict drug-induced bile duct injury.
Keywords: organoids, bile duct, cholangiocytes