Researchers at Waseda University, led by Assistant Professor Kosuke Kataoka, conducted a study published in BMC Biology that explores the development of brain organoids. The study focused on strategies to vascularize cerebral organoids and their impact on neural and vascular cell populations. Vascularization plays a crucial role in brain organoid development, and this research sheds light on its significance.
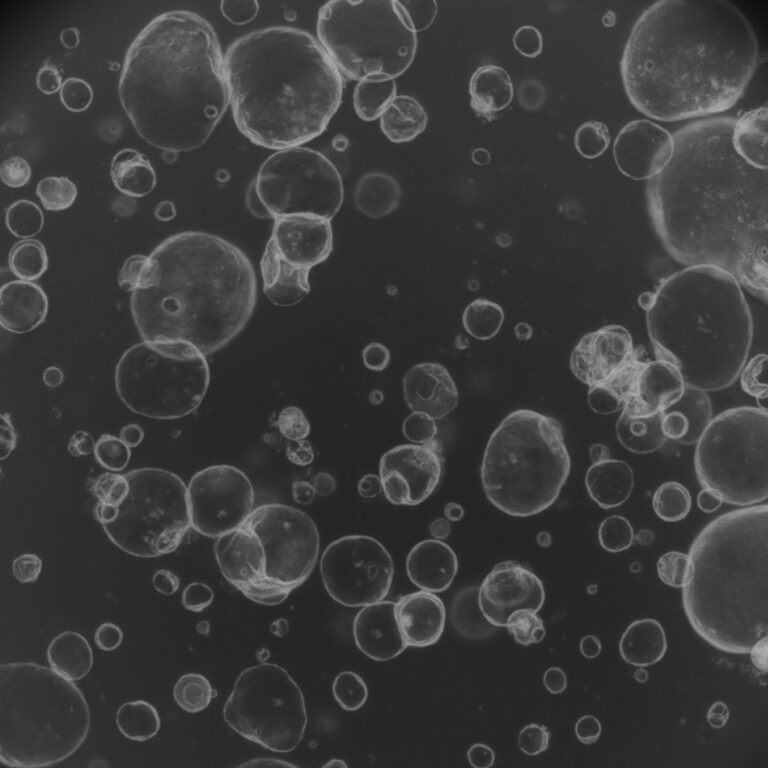
Cerebral organoids are in vitro cultured brains that mimic human brain activities, aiding in understanding evolution, disease pathogenesis, and neurodevelopment. However, they face limitations due to the absence of functional vasculature, which restricts their growth and differentiation.
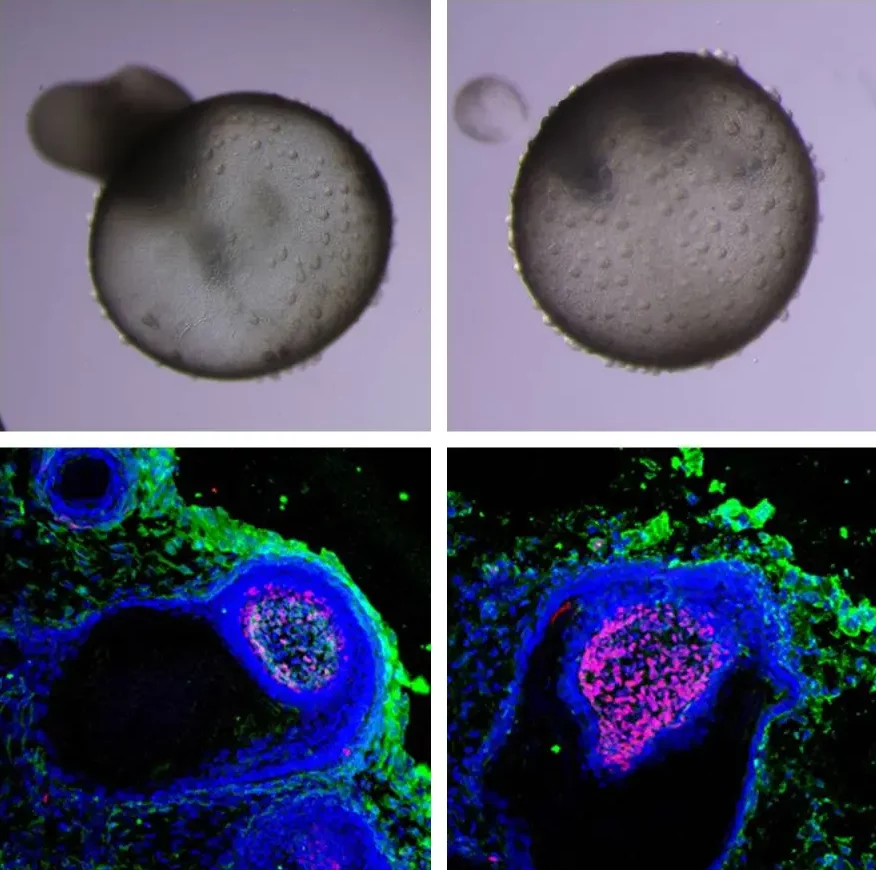
Assistant Professor Kataoka and his team conducted a comprehensive investigation into various vascularization strategies for cerebral organoids. They used single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data to evaluate these strategies and compared them to fetal brain data. The study found that all vascularization protocols improved gene expression profiles, making organoids more similar to fetal human brains.
Additionally, the study highlighted the importance of interactions between vascular-like cells and neurons for developing cerebrovascular-specific functions, like the blood-brain barrier.
These findings have potential applications in creating more realistic human brain models with blood vessels, aiding in understanding the human brain and advancing research on brain diseases and drug screening.
Keywords: Organoid, brain, vascularization, neurodevelopment