ADK Fusions Drive Progression and Therapy Resistance in HR+/HER2‒ Breast Cancer
Journal: Cell Discovery
Author: Ou-Yang, Y., Ma, D., Lin, CJ. et al., China
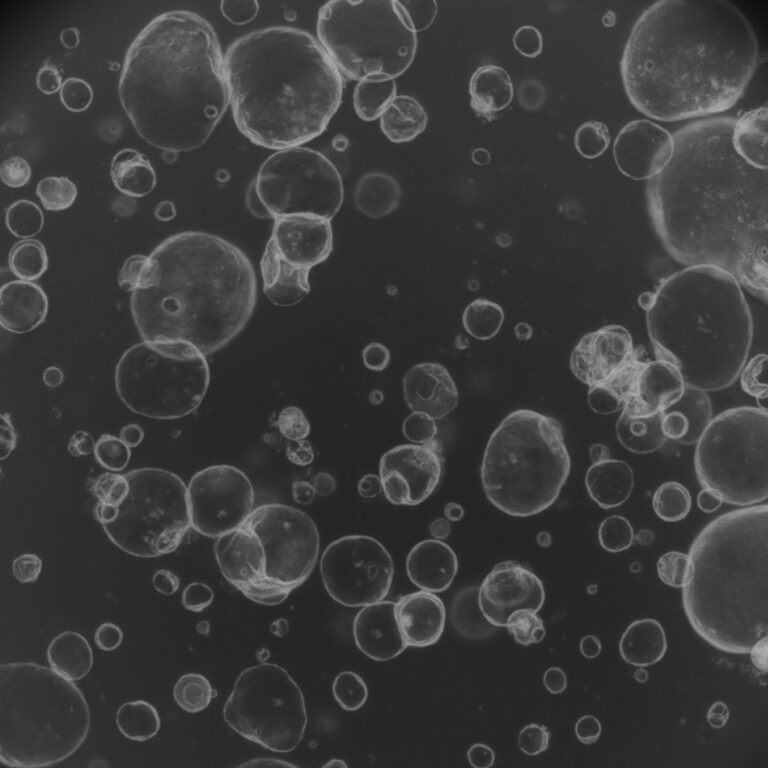
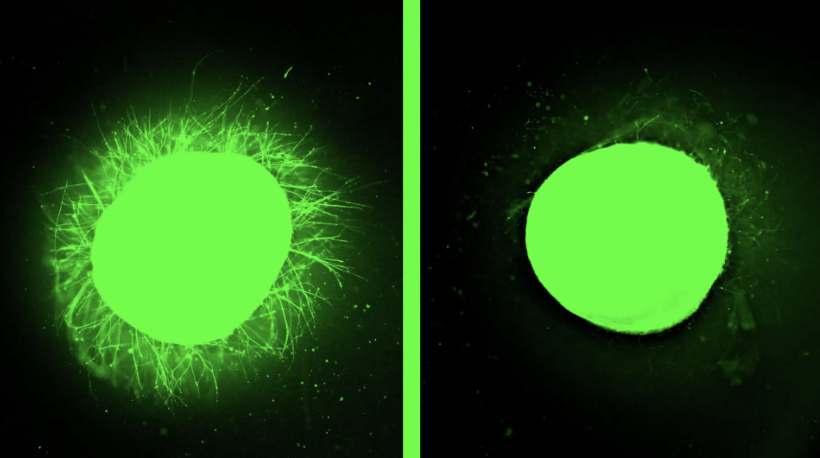
A large-scale multiomics study identified ADK fusion genes, particularly KAT6B::ADK, as recurrent drivers in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. These fusions enhance metastasis and tamoxifen resistance by activating ADK kinase through phase separation and stress response signaling. Importantly, patient-derived organoids carrying these fusions showed heightened sensitivity to ADK inhibitors, highlighting their potential as novel therapeutic targets for precision treatment.
CDK7 Inhibition Suppresses Tumor Growth in Head and Neck Cancer
Journal: Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
Author: Otero-Rosales, M., Álvarez-González, M., Pazos, I. et al., Spain
A whole-genome CRISPR screen identified CDK7 as an essential and targetable gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Inhibition of CDK7, through genetic knockout or selective inhibitors, caused cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and robust tumor suppression in HNSCC cell lines, patient-derived organoids, and xenograft models. These results position CDK7-targeted therapy as a promising strategy for treating HNSCC and warrant its advancement to clinical testing.
Pan-Cancer Analysis of Cellular Senescence Reveals Prognostic and Therapeutic Insights
Journal: Scientific Reports
Author: Chen, L., Yang, T., Zhang, Z. et al., China
This pan-cancer study characterized five distinct cellular senescence (CS) subgroups across 33 cancer types, each with unique biological features, immune profiles, and associations with prognosis and therapy response. Single-cell and multi-omics analyses confirmed CS heterogeneity and its links to tumor microenvironment, microbiota, and drug sensitivity. A machine-learning model based on CS-related genes predicted patient outcomes and immunotherapy responses, highlighting potential therapeutic targets for personalized cancer treatment.
ELLA Maps Subcellular Gene Expression in High-Resolution Spatial Transcriptomics
Journal: Nature Communications
Author: Wang, J.X., Zhou, X. ELLA, USA
ELLA is a statistical framework that models subcellular mRNA localization and identifies spatially variable genes within cells using high-resolution spatial transcriptomics data. It links gene localization patterns to mRNA characteristics and detects dynamic changes across the cell cycle. ELLA provides a robust and scalable tool for analyzing spatial gene expression at the subcellular level, enabling deeper insights into cellular function and organization.