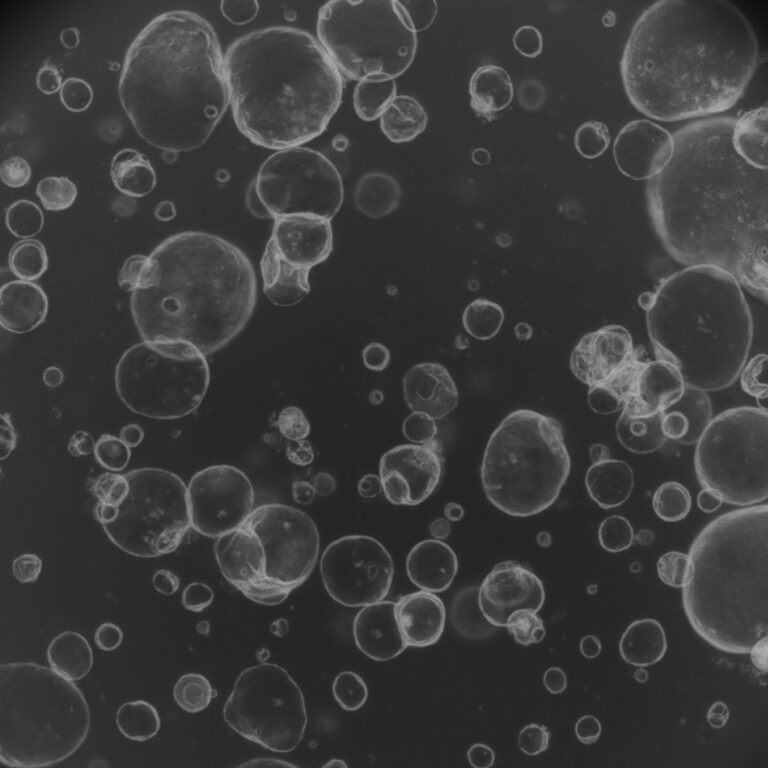
Bioartificial Liver: Organoids Meet Extracorporeal Therapy
Journal: Journal of Hepatology
Author: Yamaguchi, Hitomi et al.
Acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure remain among the deadliest clinical emergencies – with limited treatment options beyond transplantation. A new study led by Hitomi Yamaguchi (mentored by Yosuke Yoneyama) and collaborators from Osaka University, Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo), Cincinnati Children’s, and Kanzo Biomedicines, published in the Journal of Hepatology, introduces a breakthrough approach: a bioartificial liver device that works like dialysis – but for the liver. This innovative system, called UTOpiA, combines HLA-null iPSC-derived liver organoids with granulocyte-monocyte apheresis (GMA), creating a tandem circuit that both detoxifies blood and suppresses inflammation.
Elevated AMPA Receptors Linked to Long COVID Brain Fog
Journal: Brain Communications, 2025
Author: Yu Fujimoto, Hiroki Abe, Tsuyoshi Eiro et al.
Researchers found that people with long COVID – related cognitive impairment show a widespread increase in AMPA receptors, key proteins for brain signaling. This overactivation may cause disrupted information processing and neuronal stress, explaining symptoms like memory loss and brain fog. The findings also highlight [11C]K-2 PET imaging as a potential diagnostic tool and point to AMPAR blockers such as perampanel as possible treatments.
Engineered CAR-T Cells Deliver IL-12 Directly to Tumors, Boosting Safety and Efficacy
Journal: Nat. Biomed. Eng (2025)
Author: Murad, J.P., Christian, L., Rosa, R. et al.
Researchers have developed a new CAR-T cell therapy designed to overcome the challenges of treating solid tumors. By engineering CAR-T cells to secrete fusion proteins that combine the immune checkpoint blocker PD-L1 antibody fragments (αPD-L1) with interleukin-12 (IL-12), the team achieved targeted immune activation directly within the tumor microenvironment. This localized IL-12 delivery boosts immune cell infiltration and tumor destruction while minimizing systemic inflammation. In prostate and ovarian cancer models, these αPD-L1–IL-12 CAR-T cells showed superior safety and antitumor efficacy compared to traditional CAR-T cells or those modified with other cytokine fusions. The approach offers a promising strategy to make CAR-T therapies more effective for solid cancers.
Reprogramming the Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment: Turning Cold Tumors Hot
Journal: Kung, HC., Zheng, K.W., Zimmerman, J.W. et al.
Author: Nat Rev Clin Oncol (2025)
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the most treatment-resistant cancers, largely due to its complex and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME). Dense fibrotic stroma, diverse fibroblast populations, and immune cell exclusion all work together to block drug delivery and suppress antitumor immunity. Recent advances in single-cell spatial omics, machine learning, and improved PDAC models are helping researchers unravel this complexity. New strategies aim to “heat up” the cold TME – by reprogramming myeloid cells, reversing T cell exhaustion, and targeting specific fibroblast subtypes. Scientists are also exploring how metabolic crosstalk and KRAS signaling shape the tumor niche, paving the way for combination therapies that remodel the TME and enhance immunotherapy effectiveness.