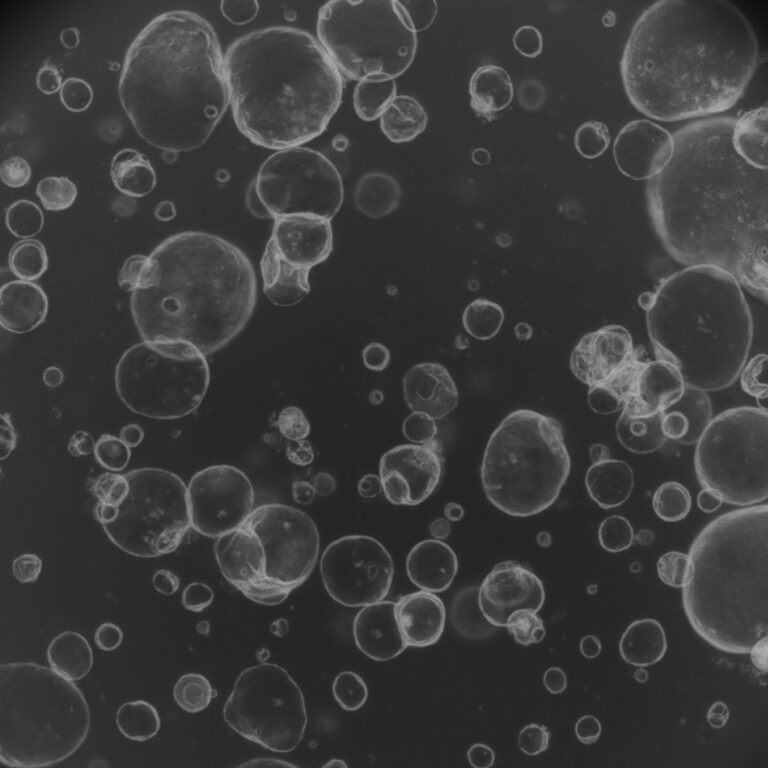
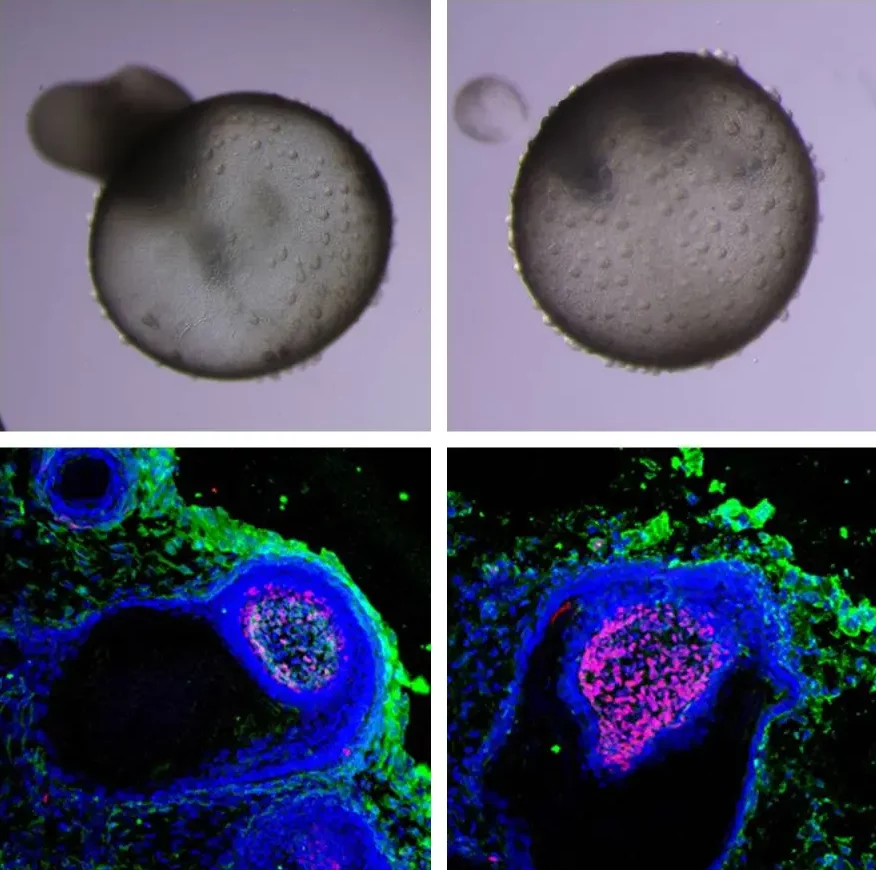
Spatiotemporal Clues to Early Gastric Cancer
Journal: Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2025).
Author: Gao, P., Zuo, C., Yuan, W. et al., China
AI-guided multi-omics mapping of early gastric lesions uncovered a NAD-dependent immunosuppressive niche that drives malignant transformation. Inflammatory pit mucous cells activate NAMPT and AREG signaling with fibroblasts and macrophages, triggering key cancer pathways (JAK-STAT, MAPK, NFκB). Blocking these signals in organoids and mouse models reduced PD-L1 expression and delayed tumor initiation, highlighting new markers and intervention targets for early detection and prevention.
Nasal Bacteria Linked to Depression
Journal: Nature Microbiology (2025).
Author: Xiang, G., Wang, Y., Ni, K. et al., China / USA
Human and mouse studies reveal that Staphylococcus aureus in the nasal microbiome can promote depression by degrading sex hormones. Patients with higher S. aureus levels showed lower nasal estradiol and testosterone, and microbiota transplants reproduced depression-like behaviors in mice. The bacterium’s enzyme Hsd12 breaks down these hormones, reducing brain dopamine and serotonin, highlighting a nose–brain pathway in mood regulation.
Cholesterol Fuels Post-Stroke Inflammation
Journal: Nature Metabolism (2025).
Author: Zhao, Q., Li, J., Feng, J. et al., China
Stroke triggers persistent microglial activation and cholesterol buildup, creating foamy microglia that sustain chronic neuroinflammation and block brain repair. Single-cell profiling linked this cholesterol metabolic reprogramming to long-term damage. Activating the enzyme CYP46A1 to reduce cholesterol overload in mice dampened inflammation and improved recovery, pointing to cholesterol metabolism as a promising target for post-stroke therapy.
Neutrophils Drive Long COVID Inflammation
Journal: Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2025).
Author: Yu, M., Hwang, S., Jang, H. et al. , Republic of Korea
In a hamster model of post-acute SARS-CoV-2 sequelae (PASC), survivors showed persistent lung damage, neutrophil accumulation, and prolonged inflammatory gene activity. Single-cell analysis revealed disrupted myeloid differentiation and lingering viral antigen. Blocking neutrophil activity – especially with the elastase inhibitor Sivelestat – reduced chronic inflammation and improved recovery, highlighting neutrophils as key therapeutic targets for long COVID.