As a virus-infected model, the utilization of tonsil, adenoid, and lung organoids allows for the evaluation of antiviral drug efficacy and facilitates virus research.

Infectious disease
This model allows researchers to study the dynamics of viral entry, replication, and host response within the tonsil organoid system.
Lambda provides a comprehensive solution, offering the service of applying antiviral treatments such as Remdesivir.
This allows for an investigation into their therapeutic efficacy in reducing viral replication.
Cell Type
· ASC
Organoid type
· Tonsil organoid
This model allows researchers to study the dynamics of viral entry, replication, and host response within the adenoid organoid system.
Lambda provides a comprehensive solution, offering the service of applying antiviral treatments.
This allows for an investigation into their therapeutic efficacy in reducing viral replication.
Cell Type
· ASC
Organoid type
· Adenoid organoid
Lung organoids, mimicking the human lung, are instrumental in respiratory infection research.
Lambda specifically employs patient-derived lung organoids for assessing the effectiveness of antiviral drugs.
This approach enhances our understanding of disease pathogenesis, aids in drug discovery, contributes to vaccine development, and provides a physiologically relevant platform for studying host-pathogen interactions.
Cell Type
· ASC
Organoid type
· Lung organoid
Lung organoids, mimicking the human lung, are instrumental in respiratory infection research.
Lambda specifically employs patient-derived lung organoids for assessing the effectiveness of antiviral drugs.
This approach enhances our understanding of disease pathogenesis, aids in drug discovery, contributes to vaccine development,
and provides a physiologically relevant platform for studying host-pathogen interactions.

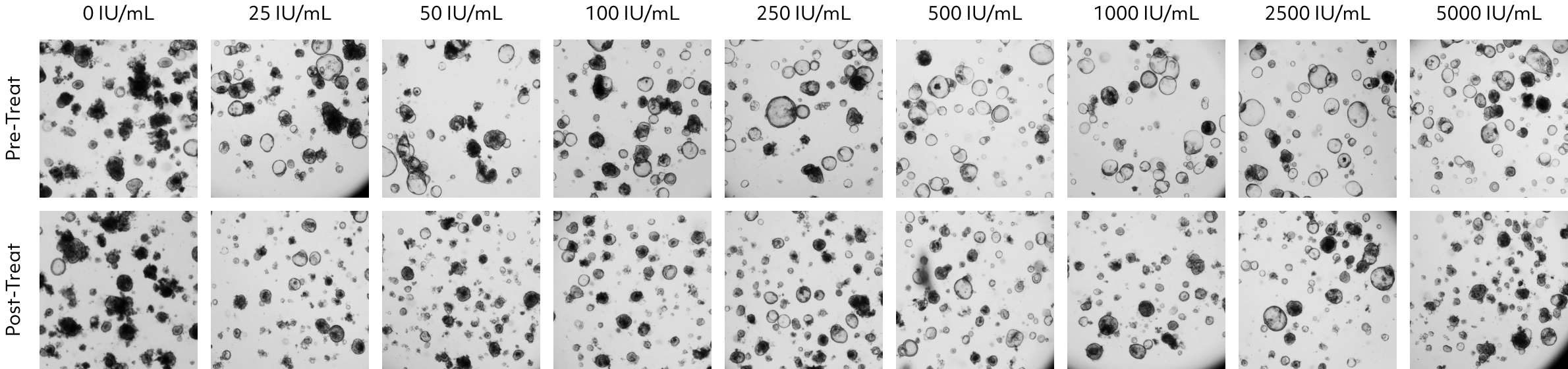
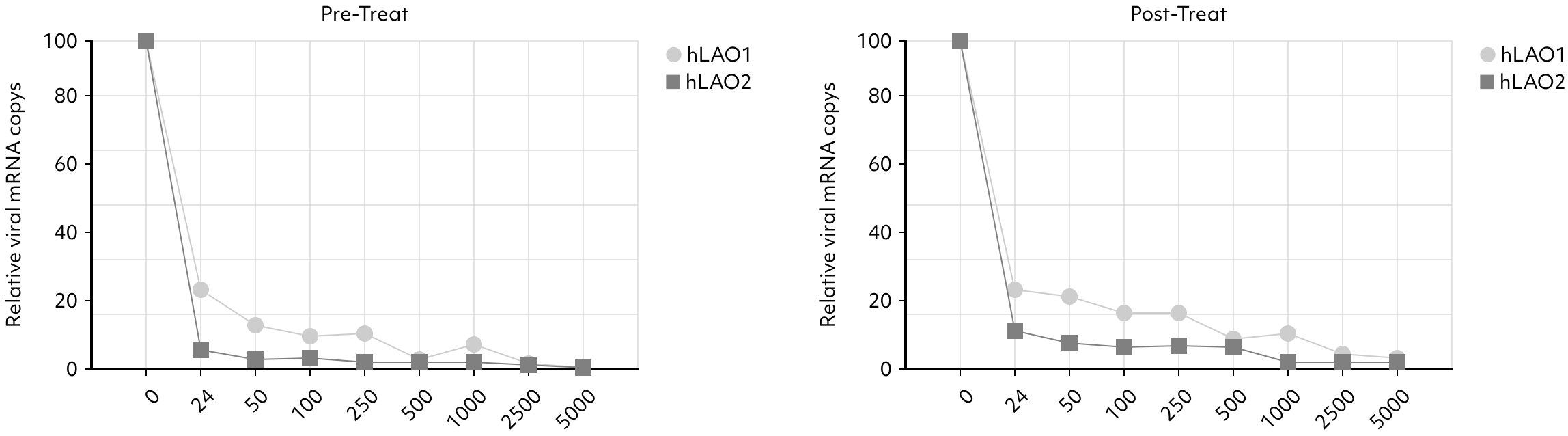
The lung organoids underwent treatment with an anti-viral drug, both before and after virus infection, with observations conducted at different drug concentrations.
As the drug concentration increased, there was a notable trend of decreasing virus titers, confirming the drug’s effectiveness in reducing the viral presence.