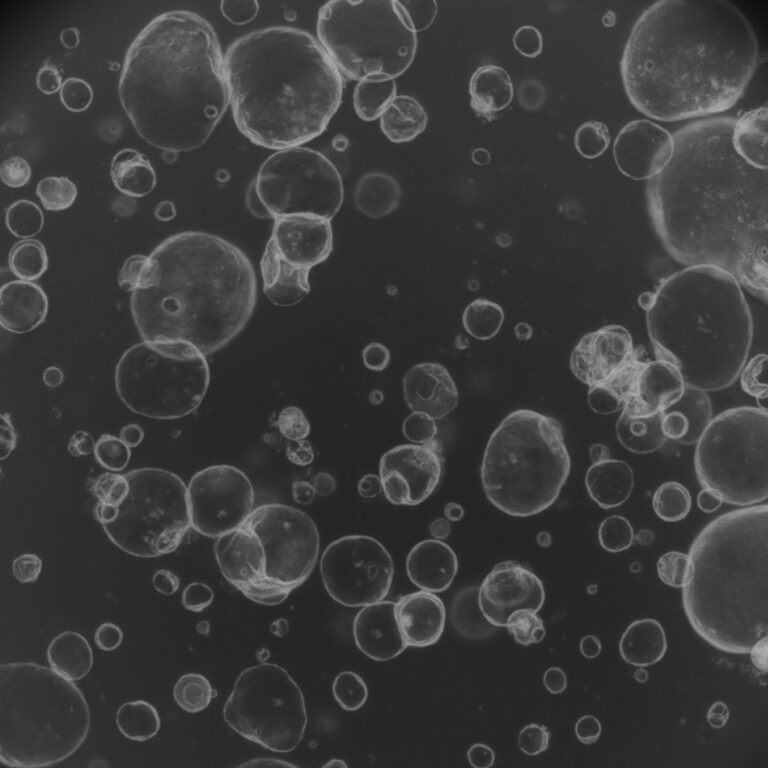
A quantitative spatial cell-cell colocalizations framework enabling comparisons between in vitro assembloids and pathological specimens
Journal: Nature Communications
Author: Gina Bouchard et al., USA
The study introduces a framework for analyzing spatial relationships between cells, particularly in lung cancer. The research validates that lab-grown “assembloids” mirror real tumor spatial organization and reveals novel insights about drug resistance patterns in cancer tissue architecture.
Development of a Rabbit Model for Adrenoleukodystrophy: A Pilot Study on Gene Therapy Using rAAV9
Journal: Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
Author: Xiaoya Zhou et al., China
Scientists developed a new rabbit model for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy using CRISPR gene editing. The model shows key disease features like elevated fatty acids and brain changes. Tests of gene therapy in these rabbits showed promising results in reducing harmful fatty acid accumulation.
Mapping T cell dynamics to molecular profiles through behavior-guided transcriptomics
Journal: Nature Protocols
Author: A. K. L. Wezenaar et al., The Netherlands
A new protocol combines live cell imaging with single-cell RNA sequencing to study T cell behavior in cancer immunotherapy. Called Behavior-Guided Transcriptomics (BGT), it reveals genetic patterns linked to T cell effectiveness against tumors, potentially improving cancer treatments.
Randomizing the human genome by engineering recombination between repeat elements
Journal: Science
Author: Jonas Koeppel et al., Germany
Scientists developed a new technique to study non-coding DNA by inserting recombination sites into human genomes. Using prime editing and CRISPR, they created cells with over 100 DNA rearrangements, revealing insights about essential genes and genome organization.