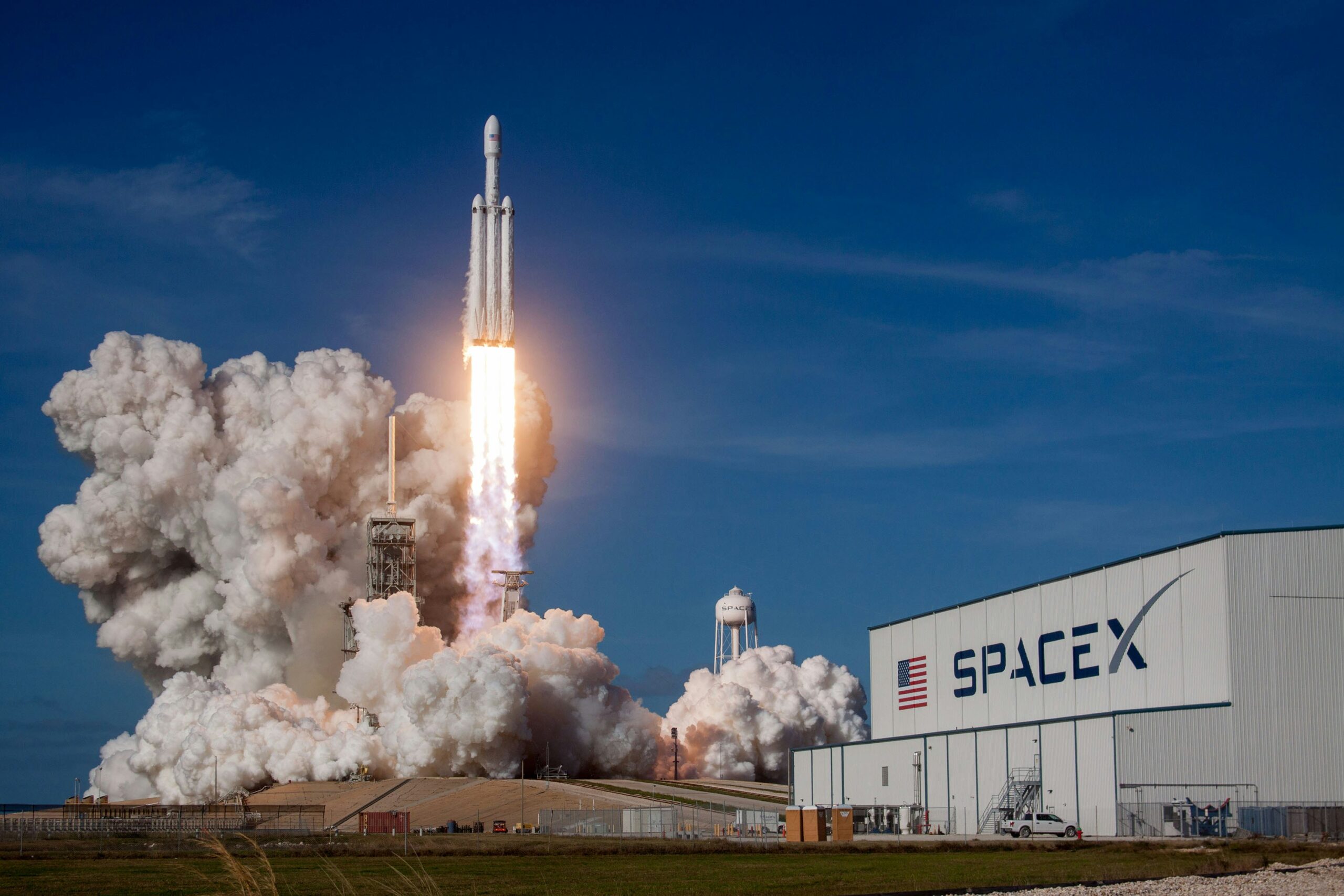
A new chapter in human space exploration has opened. If in 1969 humans landed on the moon, in 2024 humanity caught a Super Heavy booster with the launch tower’s ‘chopsticks’.
On October 13, SpaceX’s space experiment was broadcast live around the world. This event, which was as smooth as a movie, encompassed several global trends and issues.
First, efforts were made to address environmental and safety concerns related to sonic booms and the water deluge system during launch. The return of the Super Heavy booster is also for reuse, which is linked to environmental issues. Another aspect connects to space life science research.
At the end of 2023, SpaceX brought back results of life science experiments conducted on the International Space Station (ISS). This research focused on analyzing the effects of microgravity on human cells in space. The results of research in microgravity are considered a major step forward in life sciences.
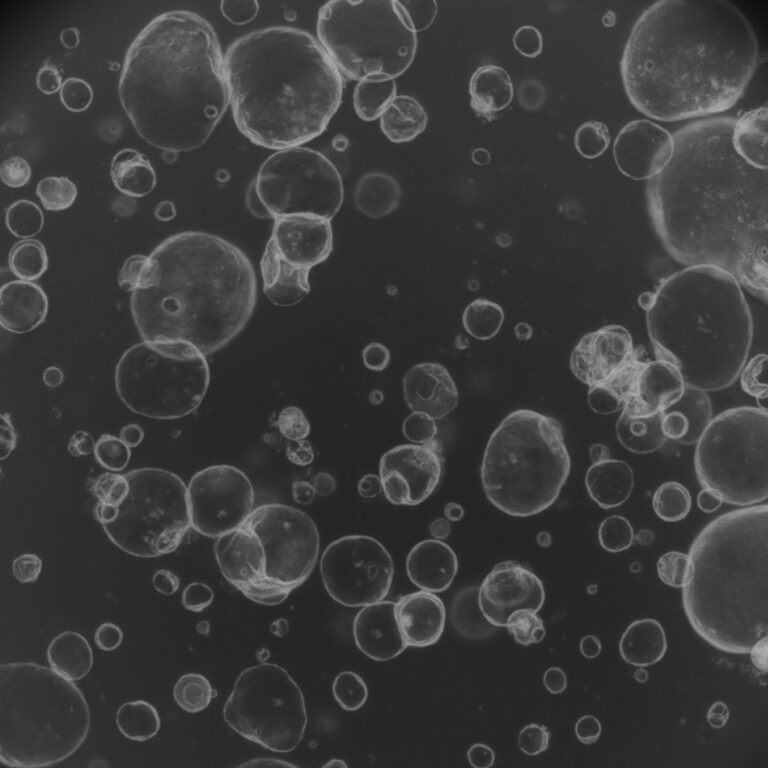
Notably, a significant study involves modeling brain and heart diseases using 3D immune liver tissue chips and stem cell-derived brain organoids. The microgravity environment in space can accelerate cell aging or disease progression faster than on Earth, providing new insights into studying diseases such as aging, neurodegenerative disorders, and heart diseases. In particular, research in space is expected to deepen our understanding of the causes and progression of diseases like dementia and Alzheimer’s.
Furthermore, SpaceX is collaborating with NASA on projects studying the growth and function of heart muscle cells and brain cells. This can contribute to finding ways to maintain human health in space environments in the long term. These studies have great potential not just for space exploration, but also for treating diseases and developing new drugs on Earth. The fusion of space biology and medicine is opening new possibilities in life science research.
The research was conducted as part of NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) mission, and scientific achievements are continuously being made through collaboration between SpaceX and the International Space Station. Space biology research is no longer just a matter of scientific curiosity but is making significant contributions to disease treatment and medical advancements on Earth.